Diabetes and coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): Molecular mechanism of Metformin intervention and the scientific basis of drug repurposing
- PMID: 34157054
- PMCID: PMC8219155
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009634
Diabetes and coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2): Molecular mechanism of Metformin intervention and the scientific basis of drug repurposing
Abstract
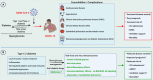
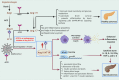
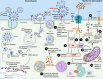
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by a new strain of coronavirus called Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), was declared a pandemic by WHO on March 11, 2020. Soon after its emergence in late December 2019, it was noticed that diabetic individuals were at an increased risk of COVID-19-associated complications, ICU admissions, and mortality. Maintaining proper blood glucose levels using insulin and/or other oral antidiabetic drugs (such as Metformin) reduced the detrimental effects of COVID-19. Interestingly, in diabetic COVID-19 patients, while insulin administration was associated with adverse outcomes, Metformin treatment was correlated with a significant reduction in disease severity and mortality rates among affected individuals. Metformin was extensively studied for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, immunomodulatory, and antiviral capabilities that would explain its ability to confer cardiopulmonary and vascular protection in COVID-19. Here, we describe the various possible molecular mechanisms that contribute to Metformin therapy's beneficial effects and lay out the scientific basis of repurposing Metformin for use in COVID-19 patients.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Timeline of WHO’s response to COVID-19. 2020 [cited 2021 Feb 10]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/29-06-2020-covidtimeline.
-
- JHU. Coronavirus Resource Center. 2021 [cited 2021 May 16]. Available from: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/.
-
- Chen Y, Gong X, Wang L, Guo J. Effects of hypertension, diabetes and coronary heart disease on COVID-19 diseases severity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. medRxiv. 2020:2020.03.25.20043133.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

