The role of PLCγ2 in immunological disorders, cancer, and neurodegeneration
- PMID: 34157287
- PMCID: PMC8318911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100905
The role of PLCγ2 in immunological disorders, cancer, and neurodegeneration
Abstract
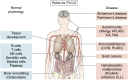
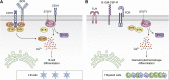
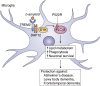
Phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase Cγ2 (PLCγ2) is a critical signaling molecule activated downstream from a variety of cell surface receptors that contain an intracellular immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif. These receptors recruit kinases such as Syk, BTK, and BLNK to phosphorylate and activate PLCγ2, which then generates 1D-myo-inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate and diacylglycerol. These well-known second messengers are required for diverse membrane functionality including cellular proliferation, endocytosis, and calcium flux. As a result, PLCγ2 dysfunction is associated with a variety of diseases including cancer, neurodegeneration, and immune disorders. The diverse pathologies associated with PLCγ2 are exemplified by distinct genetic variants. Inherited mutations at this locus cause PLCγ2-associated antibody deficiency and immune dysregulation, in some cases with autoinflammation. Acquired mutations at this locus, which often arise as a result of BTK inhibition to treat chronic lymphocytic leukemia, result in constitutive downstream signaling and lymphocyte proliferation. Finally, a third group of PLCγ2 variants actually has a protective effect in a variety of neurodegenerative disorders, presumably by increased uptake and degradation of deleterious neurological aggregates. Therefore, manipulating PLCγ2 activity either up or down could have therapeutic benefit; however, we require a better understanding of the signaling pathways propagated by these variants before such clinical utility can be realized. Here, we review the signaling roles of PLCγ2 in hematopoietic cells to help understand the effect of mutations driving immune disorders and cancer and extrapolate from this to roles which may relate to protection against neurodegeneration.
Keywords: cancer; immunodeficiency; inflammation; neurodegeneration; phospholipase C.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest S. L. M. is a scientific advisor for IFM Therapeutics. J. T. J., E. M., and S. L. N. declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Berridge M.J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993;361:315–325. - PubMed
-
- Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C and lipid signaling for sustained cellular responses. FASEB J. 1995;9:484–496. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez D., Egan S.E., Yulug I.G., Fisher E.M. Mapping the gene that encodes phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C-gamma 2 in the human and the mouse. Genomics. 1994;23:504–507. - PubMed
-
- Koss H., Bunney T.D., Behjati S., Katan M. Dysfunction of phospholipase Cγ in immune disorders and cancer. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014;39:603–611. - PubMed
-
- Walliser C., Retlich M., Harris R., Everett K.L., Josephs M.B., Vatter P., Esposito D., Driscoll P.C., Katan M., Gierschik P., Bunney T.D. Rac regulates its effector phospholipase Cgamma2 through interaction with a split pleckstrin homology domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:30351–30362. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

