New homozygous gpt delta transgenic rat strain improves an efficiency of the in vivo mutagenicity assay
- PMID: 34158118
- PMCID: PMC8220708
- DOI: 10.1186/s41021-021-00195-1
New homozygous gpt delta transgenic rat strain improves an efficiency of the in vivo mutagenicity assay
Abstract
Background: Gene mutation assays in transgenic rodents are useful tools to investigate in vivo mutagenicity in a target tissue. Using a lambda EG10 transgene containing reporter genes, gpt delta transgenic mice and rats have been developed to detect point mutations and deletions. The transgene is integrated in the genome and can be rescued through an in vitro packaging reaction. However, the packaging efficiency is lower in gpt delta rats than in mice, because of the transgene in gpt delta rats being heterozygous and in low copy number. To improve the packaging efficiency, we herein describe a newly developed homozygous gpt delta rat strain.
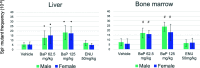
Results: The new gpt delta rat has a Wistar Hannover background and has been successfully maintained as homozygous for the transgene. The packaging efficiency in the liver was 4 to 8 times higher than that of existing heterozygous F344 gpt delta rats. The frequency of gpt point mutations significantly increased in the liver and bone marrow of N-nitroso-N-ethylurea (ENU)- and benzo[a]pyrene (BaP)-treated rats. Spi- deletion frequencies significantly increased in the liver and bone marrow of BaP-treated rats but not in ENU-treated rats. Whole genome sequencing analysis identified ≥ 30 copies of lambda EG10 transgenes integrated in rat chromosome 1.
Conclusions: The new homozygous gpt delta rat strain showed a higher packaging efficiency, and could be useful for in vivo gene mutation assays in rats.
Keywords: Spi− assay; gpt assay; gpt delta transgenic rat; mutant frequency; mutation spectrum.
Conflict of interest statement
SF, SY, HT are employed person in the company breeding and supplying
Figures




References
-
- OECD. Test No. 488: Transgenic Rodent Somatic and Germ Cell Gene Mutation Assays. OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals, Sec. 4: OECD Publishing, Paris; 2020. 10.1787/9789264203907-en.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

