Ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injections for post-traumatic greater occipital neuralgia: study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 34158124
- PMCID: PMC8218409
- DOI: 10.1186/s40814-021-00867-3
Ultrasound-guided platelet-rich plasma injections for post-traumatic greater occipital neuralgia: study protocol for a pilot randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Post-traumatic headaches (PTH) are a common sequelae of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and greatly impact patient function and quality of life. Post-traumatic greater occipital neuralgia (GON) is a type of post-traumatic headache. Conventional treatment includes steroid/anesthetic injections which typically alleviate pain but have a short duration of effect. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is an emerging biological treatment for numerous degenerative disorders, including peripheral nerve disorders. The primary aim of this pilot study is to evaluate whether a randomized control trial of PRP for the treatment of GON in patients with post-traumatic headaches is feasible in regard to recruitment, adherence, retention, and adherence and adverse events. Exploratory aims include improvement in pain, function, and quality of life in patients with post-traumatic GON receiving PRP compared to steroid/anesthetic and normal saline injections.
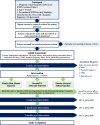
Methods: Thirty adults (over 18 years of age) with post-traumatic GON will be randomized into one of three groups: (1) autologous PRP injection, (2) steroid/anesthetic injection (standard care), or (3) placebo injection with normal saline. Injections will be performed to the greater occipital nerve under ultrasound guidance by a trained physician. Daily headache intensity and frequency data will be collected pre-injection and for the duration of the study period. Feasibility will be defined as greater than 30% recruitment, 70% completion of intervention, 70% retention, and less than 2 minor adverse events. Exploratory outcomes will be explored using the Headache Impact Test-6 (HIT-6, a valid and reliable 6-item questionnaire for assessment of the impact of headaches across different diagnostic groups of headaches) and the quality of life in following brain injury questionnaire (QOILIBRI).
Discussion: This pilot study will be the first to evaluate the feasibility of PRP as a potential treatment of GON in patients with post-traumatic headache.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov - NCT04051203 (registered August 9, 2019).
Keywords: Concussion; Corticosteroids; Greater occipital neuralgia; Platelet-rich plasma; Post-traumatic headaches; Randomized controlled trial; Traumatic brain injury; Ultrasound guidance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Similar articles
-
Ultrasound guided platelet rich plasma injections for post-traumatic greater occipital neuralgia following concussion: a pilot randomized controlled trial.Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 7;15:1400057. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1400057. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38911584 Free PMC article.
-
A double blind randomised control trial investigating the efficacy of platelet rich plasma versus placebo for the treatment of greater trochanteric pain syndrome (the HIPPO trial): a protocol for a randomised clinical trial.Trials. 2018 Sep 21;19(1):517. doi: 10.1186/s13063-018-2907-x. Trials. 2018. PMID: 30241561 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of two ultrasound-guided techniques for greater occipital nerve injections in chronic migraine: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial.Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019 May;44(5):595-603. doi: 10.1136/rapm-2018-100306. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2019. PMID: 30886069 Clinical Trial.
-
The Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Tendinopathy: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials.Am J Sports Med. 2017 Jan;45(1):226-233. doi: 10.1177/0363546516643716. Epub 2016 Jul 21. Am J Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 27268111
-
Part I--Evaluation of pediatric post-traumatic headaches.Pediatr Neurol. 2015 Mar;52(3):263-9. doi: 10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2014.10.013. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Pediatr Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25701185 Review.
Cited by
-
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) in nerve repair.Regen Ther. 2024 Apr 4;27:244-250. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2024.03.017. eCollection 2024 Dec. Regen Ther. 2024. PMID: 38586873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound guided platelet rich plasma injections for post-traumatic greater occipital neuralgia following concussion: a pilot randomized controlled trial.Front Neurol. 2024 Jun 7;15:1400057. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1400057. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38911584 Free PMC article.
-
The safety and feasibility of transcranial direct current stimulation combined with conservative treatment for patients with cervicogenic headaches: A double-blinded randomized control study protocol.Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2024 Sep 19;42:101370. doi: 10.1016/j.conctc.2024.101370. eCollection 2024 Dec. Contemp Clin Trials Commun. 2024. PMID: 39391228 Free PMC article.
-
The safety and feasibility of transcranial direct current stimulation and exercise therapy for the treatment of cervicogenic headaches: A randomized pilot trial.Headache. 2025 May;65(5):845-862. doi: 10.1111/head.14887. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Headache. 2025. PMID: 39825590 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Coronado VG, Xu L, Basavaraju SV, McGuire LC, Wald MM, Faul MD, et al. Surveillance for traumatic brain injury-related deaths--United States, 1997-2007. MMWR Surveill Summ. 2011;60(5):1–32. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials