Diffusion and adoption of the surgical robot in urology
- PMID: 34159097
- PMCID: PMC8185660
- DOI: 10.21037/tau.2019.11.33
Diffusion and adoption of the surgical robot in urology
Abstract
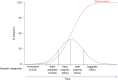
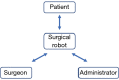
Over the last two decades, robotic surgery has become a mainstay in hospital systems around the world. Leading this charge has been Intuitive Surgical Inc.'s da Vinci robotic system (Sunnyvale, CA, USA). Through its innovative technology and unique revenue model, Intuitive has installed 4,986 robotic surgical systems worldwide in the last two decades. The rapid rate of adoption and diffusion of the surgical robot has been propelled by many important industry-specific factors. In this review, we propose a model that explains the successful adoption of robotic surgery due to its three core groups: the surgeon, the hospital administrator, and the patient.
Keywords: Robotic surgery; da Vinci robot; intuitive surgical; robotic prostatectomy; technology adoption.
2021 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tau.2019.11.33). The series “Controversies in Minimally Invasive Urologic Oncology” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Green PS. Telepresence: dexterous procedures in a virtual operating field. Surgical Endoscopy 1991;57:192.
-
- Schneeberger EW, Michler RE. An overview of the intuitive system: the surgeon’s perspective. Operative Techniques in Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 2001;6:170-6. 10.1053/otct.2001.26962 - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
