Metabolic depletion of synaptosomal enzymes linked with neurotoxicity and ovarian dysfunction by phenolic antioxidants of Croton zambsicus leaves in rats exposed to chronic mixture of anthropogenic toxicant
- PMID: 34159306
- PMCID: PMC8193606
- DOI: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100097
Metabolic depletion of synaptosomal enzymes linked with neurotoxicity and ovarian dysfunction by phenolic antioxidants of Croton zambsicus leaves in rats exposed to chronic mixture of anthropogenic toxicant
Abstract
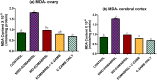
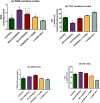
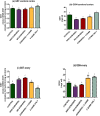
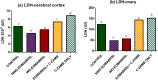
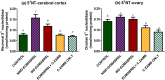
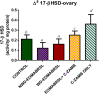
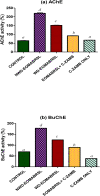
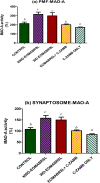
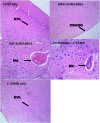
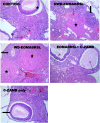
A complex mixture of organic contaminants and metals is associated with neuron-fertility disorders and studies have demonstrated that phenolic antioxidants from herbal origin, possesses a strong protective potential. This study aimed to investigate the protection of phenolic croton zambesicus (C-ZAMB) leaves against neuro-ovarian damage in rats exposed to chronic mixture of anthropogenic toxicants (EOMABRSL). The animals were divided into five groups (n = 10): Group I was given 0.5 ml of distilled water only; Group II received 0.5 ml of EOMABRSL for 98 days; Group III received 0.5 ml of EOMABRSL for 70 days and withdrew for 28 days; Group IV received 0.5 ml of EOMABRSL for 70 days +400 mg/kg phenolic C-ZAMB for 28 days; Group V received 400 mg/kg C-ZAMB only for 28 days via oral route. Both non-withdrawal and withdrawal EOMABRSL-exposed animals exhibited neuro-ovarian impairment by up-regulating neuronal 51 eco-nucleotidase (51ENT), acetylcholinesterase (AChE), butrylcholinesterase (BuChE), synaptosomal monoamine oxidase-A (MAO-A) with altered cerebral antioxidants. Similarly, exposure to EOMABRSL for 98 and 70 days caused ovarian injury by amplifying the activity of 51ENT with corresponding decline of fertility index, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and Δ5 17β-hydroxyl steroid dehydrogenase (Δ517β-HSD). EOMABRSL intoxication also increased the neuro-ovarian MDA content with reduced numbers of neonates. Phenolic antioxidants from C-ZAMB leaves identified by High Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) ameliorated the chronic EOMABRSL intoxication. The treatment also prevented ovarian lesions by depleting MDA content and improved antioxidant status. Thus, confirming its neuro-ovarian protection.
Keywords: Animal model; Chronic mixture; Metabolic inhibition; Neuro-ovariotoxicity; Phenolic Croton zambesicus; Synaptosome.
© 2021 Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Akintunde J.K declares that he has no conflict of interest. Ibrahim L.B declares that she has no conflict of interest. Omotosho O.D declares that he has no conflict of interest. Boligon A.A declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Meta-inhibition of ocular and gastrointestinal dysfunctions by phenolic-rich fraction of Croton zambsicus leaves in a rat model exposed to chronic mixed metals.Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2021 Dec;40(4):365-375. doi: 10.1080/15569527.2021.1976792. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34488518
-
Rat liver and kidney post-mitochondrial dysfunction by addition of chronic mixed metal intoxication and hepatorenal wellness mediated by phenolic components from Croton zambiscus leaves.Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;74:103293. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2019.103293. Epub 2019 Nov 9. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31760208
-
Modulation of Cardiopulmonary Toxicity and Oxidative Stress by Phenolic-Rich Fraction of Croton zambiscus Leaves in Rat Exposed to Chronic Mixture of Environmental Toxicants.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021 Apr;21(4):272-285. doi: 10.1007/s12012-020-09618-x. Epub 2020 Nov 1. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33135141
-
Depletion of cellular adenosine triphosphate and hepatocellular damage in rat after subchronic exposure to leachate from anthropogenic recycling site.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2015 Nov;34(11):1083-95. doi: 10.1177/0960327115569809. Epub 2015 Feb 2. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2015. PMID: 25645823
-
Health benefits and phenolic compounds of Moringa oleifera leaves: A comprehensive review.Phytomedicine. 2021 Dec;93:153771. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153771. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34700271 Review.
Cited by
-
Diet patterns, gut microbiota and metabolic disorders: Perspectives and challenges.Metabol Open. 2024 Aug 8;23:100310. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2024.100310. eCollection 2024 Sep. Metabol Open. 2024. PMID: 39351486 Free PMC article.
-
Strawberry and Drupe Fruit Wines Antioxidant Activity and Protective Effect Against Induced Oxidative Stress in Rat Synaptosomes.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Jan 28;14(2):155. doi: 10.3390/antiox14020155. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002342 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rehman K., Fatima F., Waheed I., Akash M.S.H. Prevalence of exposure of heavy metals and their impact on health consequences. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119:157–184. - PubMed
-
- Akintunde J.K., Oboh G., Akindahunsi A.A. Inhibition of key markers linked with spermatogenesis and cellular ATP by sub-chronic exposure to leachate in a rat model. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2015;68:159–168. - PubMed
-
- Akintunde J.K., Oboh G. Sub-chronic exposure to leachate activates key markers linked with neurological disorder in Wistar male rat. Environ Sci Pollut Res. 2015;22:18541–18553. - PubMed
-
- Davoodi H., Esmaeili S., Mortazavian A.M. Effects of milk and milk products consumption on cancer: a review. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf. 2013;12:249–264.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

