Acquired Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibition in Cancer
- PMID: 34161704
- PMCID: PMC8864540
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2105281
Acquired Resistance to KRASG12C Inhibition in Cancer
Abstract
Background: Clinical trials of the KRAS inhibitors adagrasib and sotorasib have shown promising activity in cancers harboring KRAS glycine-to-cysteine amino acid substitutions at codon 12 (KRASG12C). The mechanisms of acquired resistance to these therapies are currently unknown.
Methods: Among patients with KRASG12C -mutant cancers treated with adagrasib monotherapy, we performed genomic and histologic analyses that compared pretreatment samples with those obtained after the development of resistance. Cell-based experiments were conducted to study mutations that confer resistance to KRASG12C inhibitors.
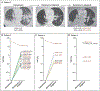
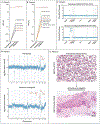
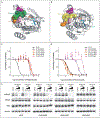
Results: A total of 38 patients were included in this study: 27 with non-small-cell lung cancer, 10 with colorectal cancer, and 1 with appendiceal cancer. Putative mechanisms of resistance to adagrasib were detected in 17 patients (45% of the cohort), of whom 7 (18% of the cohort) had multiple coincident mechanisms. Acquired KRAS alterations included G12D/R/V/W, G13D, Q61H, R68S, H95D/Q/R, Y96C, and high-level amplification of the KRASG12C allele. Acquired bypass mechanisms of resistance included MET amplification; activating mutations in NRAS, BRAF, MAP2K1, and RET; oncogenic fusions involving ALK, RET, BRAF, RAF1, and FGFR3; and loss-of-function mutations in NF1 and PTEN. In two of nine patients with lung adenocarcinoma for whom paired tissue-biopsy samples were available, histologic transformation to squamous-cell carcinoma was observed without identification of any other resistance mechanisms. Using an in vitro deep mutational scanning screen, we systematically defined the landscape of KRAS mutations that confer resistance to KRASG12C inhibitors.
Conclusions: Diverse genomic and histologic mechanisms impart resistance to covalent KRASG12C inhibitors, and new therapeutic strategies are required to delay and overcome this drug resistance in patients with cancer. (Funded by Mirati Therapeutics and others; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT03785249.).
Copyright © 2021 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures


Comment in
-
Finally, Effective Inhibitors of Mutant KRAS.N Engl J Med. 2021 Jun 24;384(25):2447-2449. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2107884. N Engl J Med. 2021. PMID: 34161711 No abstract available.
-
Uncovering adagrasib resistance.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021 Sep;18(9):541. doi: 10.1038/s41571-021-00545-6. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34267362 No abstract available.
-
The promise and peril of KRAS G12C inhibitors.Cancer Cell. 2021 Aug 9;39(8):1059-1061. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.07.011. Cancer Cell. 2021. PMID: 34375610
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
