Older patients (aged ≥60 years) with previously untreated advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma: a detailed analysis from the phase III ECHELON-1 study
- PMID: 34162178
- PMCID: PMC9052913
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2021.278438
Older patients (aged ≥60 years) with previously untreated advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma: a detailed analysis from the phase III ECHELON-1 study
Abstract
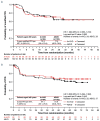
Effective and tolerable treatments are needed for older patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma. We report results for older patients with classical Hodgkin lymphoma treated in the large phase III ECHELON-1 study of frontline brentuximab vedotin plus doxorubicin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (A+AVD) versus doxorubicin, bleomycin, vinblastine, and dacarbazine (ABVD). Modified progression-free survival per independent review facility for older versus younger patients (aged ≥60 vs. <60 years) was a pre-specified subgroup analysis; as the ECHELON- 1 study was not powered for these analyses, reported P-values are descriptive. Of 1,334 enrolled patients, 186 (14%) were aged ≥60 years (A+AVD: n=84, ABVD: n=102); results below refer to this age group. Modified progression-free survival per independent review facility was similar in the two arms at 24 months (A+AVD: 70.3% [95% confidence interval (CI): 58.4-79.4], ABVD: 71.4% [95% CI: 60.5-79.8], hazard ratio (HR)=1.00 [95% CI: 0.58-1.72], P=0.993). After a median follow-up of 60.9 months, 5-year progression-free survival per investigator was 67.1% with A+AVD versus 61.6% with ABVD (HR=0.820 [95% CI: 0.494-1.362], P=0.443). Comparing A+AVD versus ABVD, grade 3/4 peripheral neuropathy occurred in 18% versus 3%; any-grade febrile neutropenia in 37% versus 17%; and any-grade pulmonary toxicity in 2% versus 13%, respectively, with three (3%) pulmonary toxicity-related deaths in patients receiving ABVD (none in those receiving A+AVD). Altogether, A+AVD showed overall similar efficacy to ABVD with survival rates in both arms comparing favorably to those of prior series in older patients with advanced-stage classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Compared to ABVD, A+AVD was associated with higher rates of neuropathy and neutropenia, but lower rates of pulmonary-related toxicity. Trials registered at ClinicalTrials.gov identifiers: NCT01712490; EudraCT number: 2011-005450-60.
Figures
References
-
- Proctor SJ, Wilkinson J, Jones G, et al. Evaluation of treatment outcome in 175 patients with Hodgkin lymphoma aged 60 years or over: the SHIELD study. Blood. 2012;119(25):6005-6015. - PubMed
-
- Stark GL, Wood KM, Jack F, et al. Hodgkin's disease in the elderly: a population-based study. Br J Haematol. 2002;119(2):432-440. - PubMed
-
- Engert A, Ballova V, Haverkamp H, et al. Hodgkin's lymphoma in elderly patients: a comprehensive retrospective analysis from the German Hodgkin's Study Group. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(22):5052-5060. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

