The INSPIRE Population Survey: development, dissemination and respondent characteristics
- PMID: 34162324
- PMCID: PMC8223353
- DOI: 10.1186/s12874-021-01329-3
The INSPIRE Population Survey: development, dissemination and respondent characteristics
Abstract
Background: Most older adults prefer to continue living at home despite increasing care needs and demand for services. To aid in maintaining independence, integrated care models for community-dwelling older people are promoted as the most cost-effective approach. The implementation of such care models is challenging and often the end-users are not involved or their needs are not considered. We conducted a population survey in order to understand the needs and preferences of home-dwelling older adults living in Canton Basel-Landschaft, Switzerland. The aims of this paper are to chronicle the development of the INSPIRE Population Survey, outline its variables and measurements, describe the marketing strategy utilized for survey dissemination and report on the response rate and respondent characteristics.
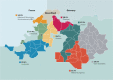
Methods: The INSPIRE Population Survey, conducted between March and August 2019, is a cross-sectional survey of older adults aged 75 and older living at home in Canton Basel-Landschaft. The questionnaire was developed by expert input and stakeholder involvement. Its readability and acceptability were pilot-tested with older people. To ensure the likelihood of a high and representative response rate, a meticulous step-by-step marketing strategy was developed prior to the dissemination of the questionnaire.
Results: The overall response rate was 30.7% (n = 8,846), with variations between 20.6 and 34.5% across the different care regions in the canton. A generally higher response rate was found in the care regions with a higher density and which bordered the urban city of Basel. We received support from local stakeholders, policy makers and media through using a broad combination of marketing channels and targeting our community partners who have a strong relationship with our target audience.
Conclusions: Although recruiting older adults in research is challenging, our study shows that a high response rate can be achieved by developing the survey through expert input and by involving all important stakeholders, including older adults, throughout the entire process.
Keywords: Aged; Community-care; Delivery of healthcare; Demographic Survey; Integrated; Stakeholder involvement; Surveys and Questionnaires.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources