Unpacking the intricacies of Rickettsia-vector interactions
- PMID: 34162522
- PMCID: PMC8344978
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pt.2021.05.008
Unpacking the intricacies of Rickettsia-vector interactions
Abstract
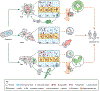
Although Rickettsia species are molecularly detected among a wide range of arthropods, vector competence becomes an imperative aspect of understanding the ecoepidemiology of these vector-borne diseases. The synergy between vector homeostasis and rickettsial invasion, replication, and release initiated within hours (insects) and days (ticks) permits successful transmission of rickettsiae. Uncovering the molecular interplay between rickettsiae and their vectors necessitates examining the multifaceted nature of rickettsial virulence and vector infection tolerance. Here, we highlight the biological differences between tick- and insect-borne rickettsiae and the factors facilitating the incidence of rickettsioses. Untangling the complex relationship between rickettsial genetics, vector biology, and microbial interactions is crucial in understanding the intricate association between rickettsiae and their vectors.
Keywords: Rickettsia; vector; vector transmission; vector–pathogen interactions.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Akram SM et al. (2020) Rickettsia Prowazekii (Epidemic Typhus). In StatPearls.
-
- Diop A et al. (2018) Rickettsial genomics and the paradigm of genome reduction associated with increased virulence. Microbes Infect 20 (7-8), 401–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

