Reactivation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by mRNA nanoparticles enhances antitumor immunity in preclinical models
- PMID: 34162754
- PMCID: PMC8284983
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aba9772
Reactivation of the tumor suppressor PTEN by mRNA nanoparticles enhances antitumor immunity in preclinical models
Abstract
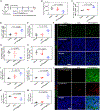
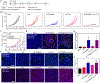
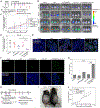
Increasing clinical evidence has demonstrated that the deletion or mutation of tumor suppressor genes such as the gene-encoding phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) in cancer cells may correlate with an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME) and poor response or resistance to immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) therapy. It is largely unknown whether the restoration of functional PTEN may modulate the TME and improve the tumor's sensitivity to ICB therapy. Here, we demonstrate that mRNA delivery by polymeric nanoparticles can effectively induce expression of PTEN in Pten-mutated melanoma cells and Pten-null prostate cancer cells, which in turn induces autophagy and triggers cell death-associated immune activation via release of damage-associated molecular patterns. In vivo results illustrated that PTEN mRNA nanoparticles can reverse the immunosuppressive TME by promoting CD8+ T cell infiltration of the tumor tissue, enhancing the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-12, tumor necrosis factor-α, and interferon-γ, and reducing regulatory T cells and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. The combination of PTEN mRNA nanoparticles with an immune checkpoint inhibitor, anti-programmed death-1 antibody, results in a highly potent antitumor effect in a subcutaneous model of Pten-mutated melanoma and an orthotopic model of Pten-null prostate cancer. Moreover, the combinatorial treatment elicits immunological memory in the Pten-null prostate cancer model.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Peng W, Chen JQ, Liu C, Malu S, Creasy C, Tetzlaff MT, Xu C, McKenzie JA, Zhang C, Liang X, Williams LJ, Deng W, Chen G, Mbofung R, Lazar AJ, Torres-Cabala CA, Cooper ZA, Chen P-L, Tieu TN, Spranger S, Yu X, Bernatchez C, Forget M-A, Haymaker C, Amaria R, McQuade JL, Glitza IC, Cascone T, Li HS, Kwong LN, Heffernan TP, Hu JH, Bassett RL Jr., Bosenberg MW, Woodman SE, Overwijk WW, Lizée G, Roszik J, Gajewski TF, Wargo JA, Gershenwald JE, Radvanyi L, Davies MA, Hwu P, Loss of PTEN promotes resistance to T cell–mediated immunotherapy. Cancer Discov. 6, 202–216 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

