Irreversible electroporation augments checkpoint immunotherapy in prostate cancer and promotes tumor antigen-specific tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells
- PMID: 34162858
- PMCID: PMC8222297
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-24132-6
Irreversible electroporation augments checkpoint immunotherapy in prostate cancer and promotes tumor antigen-specific tissue-resident memory CD8+ T cells
Abstract
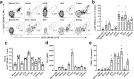
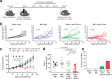
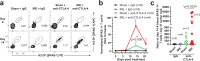
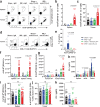
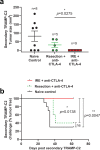
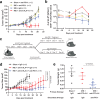
Memory CD8+ T cells populate non-lymphoid tissues (NLTs) following pathogen infection, but little is known about the establishment of endogenous tumor-specific tissue-resident memory T cells (TRM) during cancer immunotherapy. Using a transplantable mouse model of prostate carcinoma, here we report that tumor challenge leads to expansion of naïve neoantigen-specific CD8+ T cells and formation of a small population of non-recirculating TRM in several NLTs. Primary tumor destruction by irreversible electroporation (IRE), followed by anti-CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), promotes robust expansion of tumor-specific CD8+ T cells in blood, tumor, and NLTs. Parabiosis studies confirm that TRM establishment following dual therapy is associated with tumor remission in a subset of cases and protection from subsequent tumor challenge. Addition of anti-PD-1 following dual IRE + anti-CTLA-4 treatment blocks tumor growth in non-responsive cases. This work indicates that focal tumor destruction using IRE combined with ICI is a potent in situ tumor vaccination strategy that generates protective tumor-specific TRM.
Conflict of interest statement
B.F. is employed by Boston Scientific. S.R. retired from BTG plc in 2018. Both B.F. and S.R. provided conceptual and technical oversight to portions of the project. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Galluzzi, L., Chan, T. A., Kroemer, G., Wolchok, J. D. & Lopez-Soto, A. The hallmarks of successful anticancer immunotherapy. Sci. Transl. Med.10, eaat7807 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

