Experimental evidence that apologies promote forgiveness by communicating relationship value
- PMID: 34162912
- PMCID: PMC8222305
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-92373-y
Experimental evidence that apologies promote forgiveness by communicating relationship value
Abstract
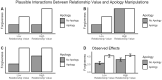
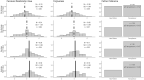
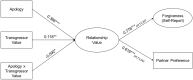
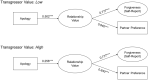
Robust evidence supports the importance of apologies for promoting forgiveness. Yet less is known about how apologies exert their effects. Here, we focus on their potential to promote forgiveness by way of increasing perceptions of relationship value. We used a method for directly testing these causal claims by manipulating both the independent variable and the proposed mediator. Namely, we use a 2 (Apology: yes vs. no) × 2 (Value: high vs. low) concurrent double-randomization design to test whether apologies cause forgiveness by affecting the same causal pathway as relationship value. In addition to supporting this causal claim, we also find that apologies had weaker effects on forgiveness when received from high-value transgressors, suggesting that the forgiveness-relevant information provided by apologies is redundant with relationship value. Taken together, these findings from a rigorous methodological paradigm help us parse out how apologies promote relationship repair.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Embodied remorse: Physical displays of remorse increase positive responses to public apologies, but have negligible effects on forgiveness.J Pers Soc Psychol. 2020 Aug;119(2):367-389. doi: 10.1037/pspi0000208. Epub 2019 Sep 12. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2020. PMID: 31512916
-
Why group apologies succeed and fail: intergroup forgiveness and the role of primary and secondary emotions.J Pers Soc Psychol. 2012 Feb;102(2):306-22. doi: 10.1037/a0024838. Epub 2011 Aug 1. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2012. PMID: 21806306
-
Costly group apology communicates a group's sincere "intention".Soc Neurosci. 2020 Apr;15(2):244-254. doi: 10.1080/17470919.2019.1697745. Epub 2019 Nov 29. Soc Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 31762397
-
An evolutionary psychology view of forgiveness: individuals, groups, and culture.Curr Opin Psychol. 2022 Apr;44:275-280. doi: 10.1016/j.copsyc.2021.09.021. Epub 2021 Oct 9. Curr Opin Psychol. 2022. PMID: 34801844 Review.
-
Eliciting forgiveness.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2021 Nov;12(6):e1572. doi: 10.1002/wcs.1572. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Cogn Sci. 2021. PMID: 34309234 Review.
Cited by
-
Psychological perspectives on divine forgiveness: seeking divine forgiveness.Front Psychol. 2024 Feb 21;15:1256402. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1256402. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38455121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McCullough ME. Beyond Revenge: The Evolution of the Forgiveness Instinct. Wiley; 2008.
-
- McCullough, M. E., Kurzban, R. & Tabakm, B. A. Cognitive systems for revenge and forgiveness. Behav. Brain Sci.36(1), 1–15 (2013). - PubMed

