Traceless parallel peptide purification by a first-in-class reductively cleavable linker system featuring a safety-release
- PMID: 34164003
- PMCID: PMC8179278
- DOI: 10.1039/d0sc06285e
Traceless parallel peptide purification by a first-in-class reductively cleavable linker system featuring a safety-release
Abstract
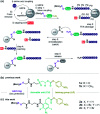
Hundreds of peptides can be synthesized by automated parallel synthesizers in a single run. In contrast, the most widely used peptide purification method - high-pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) - only allows one-by-one processing of each sample. The chromatographic purification of many peptides, therefore, remains a time-consuming and costly effort. Catch-and-release methods can be processed in parallel and potentially provide a remedy. However, no such system has yet provided a true alternative to HPLC. Herein we present the development of a side-reaction free, reductively cleavable linker. The linker is added to the target peptide as the last building block during peptide synthesis. After acidic cleavage from synthetic resin, the linker-tagged full-length peptide is caught onto an aldehyde-modified solid support by rapid oxime ligation, allowing removal of all impurities lacking the linker by washing. Reducing the aryl azide to an aniline sensitizes the linker for cleavage. However, scission does not occur at non-acidic pH enabling wash out of reducing agent. Final acidic treatment safely liberates the peptide by an acid-catalysed 1,6-elimination. We showcase this first-in-class reductively cleavable linker system in the parallel purification of a personalized neoantigen cocktail, containing 20 peptides for cancer immunotherapy within six hours.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare competing financial interests: the technology described in the manuscript is part of pending patent applications. Kit products containing linker molecule and aldehyde-modified agarose beads as presented here can be purchased at http://belyntic.com.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

