Protective effect of anisodamine on bleomycin-induced acute lung injury in immature rats via modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and cell apoptosis by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway
- PMID: 34164493
- PMCID: PMC8184412
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-21-1750
Protective effect of anisodamine on bleomycin-induced acute lung injury in immature rats via modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and cell apoptosis by inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 pathway
Abstract
Background: Pediatric acute lung injury (ALI) is one of the most common causes of infant mortality. Although lung-protective strategies have developed in recent years, no ALI treatment is currently available. Anisodamine (Ani) is a common drug used to treat gastrointestinal smooth muscle spasm. The protective effects of Ani against acute kidney injury and myocardial injury have been reported. However, the efficacy of Ani on bleomycin (BLM)-induced ALI has not been examined previously. In the present study, we aimed to examine the effects of Ani on bleomycin (BLM)-induced ALI on immature rats.
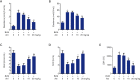
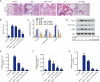
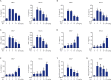
Methods: The ALI rat model was established by intratracheally administration of BLM. Ani treatment was performed by an intravenous injection at different concentrations. The lung function of each rat was measured, and then lung tissue structures, apoptosis, and collagen deposition were observed by hematoxylin-eosin staining, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated digoxigenin-dUTP nick-end labeling assay, and Masson's staining, respectively. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect the levels of inflammatory cytokines. The expression of apoptosis-related proteins and fibrosis-related markers was determined by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and/or Western blot analysis. Finally, the expression levels of Janus tyrosine kinase 2 (JAK2) and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) were determined.
Results: Our findings indicated that lung function was remarkably decreased in BLM-induced rats, which could be reversed by Ani. Ani treatment increased the levels of antioxidant enzymes, decreased the apoptotic rate and apoptosis-related proteins, and downregulated the expression of fibrosis-related markers. Additionally, Ani treatment also attenuated inflammatory response and suppressed the activation of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrated that Ani had potent activity against BLM-induced ALI in immature rats through inhibiting the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Our findings provide supporting evidence to further investigate the therapeutic effect of Ani against ALI in children.
Keywords: Anisodamine; acute lung injury (ALI); bleomycin; inflammation; oxidative stress.
2021 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-21-1750). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
