The modern approach to esophageal palliative and emergency surgery
- PMID: 34164539
- PMCID: PMC8184432
- DOI: 10.21037/atm.2020.03.107
The modern approach to esophageal palliative and emergency surgery
Abstract
Thoracic surgeons currently have multiple options and strategies to guide treatment in esophageal palliative and emergency conditions. To guide the selection of an individualized palliative approach, physicians, including thoracic surgeons, must take into consideration many factors including prognosis, performance status and comorbidities of patients. For dysphagia more specifically, esophageal stent placement is the most widely used intervention for rapidly relieving dysphagia in inoperable esophageal cancer patients. The combination of esophageal stent placement with other therapies has an impact on palliative care. Innovations including radioactive stents, drug-eluding stents and biodegradable stents will require further evaluation and validation studies. Currently, patients with inoperable esophageal cancer have access to oncological and biological therapies that are improving their prognosis. A shift toward restaging and potential curative intent is occurring in current clinical practice. In acute intrathoracic esophageal perforation cases, high index of suspicion, multidisciplinary team expertise, antibiotics and hybrid treatment strategies, have significantly improved outcomes of patients in recent years. Hybrid treatment strategies denote the combination of minimally invasive interventions for source control and endoluminal procedures to seal the esophageal perforation. Endoluminal procedures as treatment of acute intrathoracic esophageal perforation include stent placement, over-the-scope clip and endoluminal vacuum therapy. Future perspective in the management of esophageal perforation seems to be the combination of endoluminal therapies tailored to the specific clinical scenario. Thoracic surgeons benefit from mastering endoluminal therapies and advanced endoscopic techniques. An understanding of these rapidly evolving therapies, i.e., outcomes, limitations and innovations, is required to optimally manage esophageal palliative and emergency conditions.
Keywords: Esophageal cancer; dysphagia; emergency; palliation; perforation.
2021 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: Both authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm.2020.03.107). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

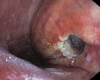
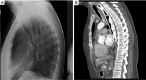
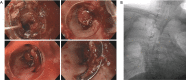
Similar articles
-
Esophageal Perforations: An Endoscopic Approach to Management.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019 Nov 20;21(11):57. doi: 10.1007/s11894-019-0730-5. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31749030 Review.
-
Endoluminal palliation for dysphagia secondary to esophageal carcinoma.Surg Clin North Am. 2002 Aug;82(4):747-61. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(02)00037-3. Surg Clin North Am. 2002. PMID: 12472128 Review.
-
Minimally invasive management of esophageal perforation.Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2018 Jul 3;26(3):496-503. doi: 10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2018.15354. eCollection 2018 Jul. Turk Gogus Kalp Damar Cerrahisi Derg. 2018. PMID: 32082789 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Esophageal stent placement for the treatment of iatrogenic intrathoracic esophageal perforation.Ann Thorac Surg. 2007 Jun;83(6):2003-7; discussion 2007-8. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2007.02.025. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007. PMID: 17532387
-
Palliative Treatment of Esophageal Cancer.Semin Radiat Oncol. 1994 Jul;4(3):202-214. doi: 10.1053/SRAO00400192. Semin Radiat Oncol. 1994. PMID: 10717108
Cited by
-
Emergent Esophagectomy in Patients with Esophageal Malignancy Is Associated with Higher Rates of Perioperative Complications but No Independent Impact on Short-Term Mortality.J Chest Surg. 2024 Mar 5;57(2):160-168. doi: 10.5090/jcs.23.149. Epub 2024 Feb 7. J Chest Surg. 2024. PMID: 38321624 Free PMC article.
-
Esophageal cancer practice guidelines 2022 edited by the Japan Esophageal Society: part 2.Esophagus. 2023 Jul;20(3):373-389. doi: 10.1007/s10388-023-00994-1. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Esophagus. 2023. PMID: 36995449 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Interventional Treatment Is an Effective Approach to Relieve Symptoms in Patients With Malignant Tracheoesophageal Fistula.Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025 Aug;8(8):e70312. doi: 10.1002/cnr2.70312. Cancer Rep (Hoboken). 2025. PMID: 40879267 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Opstelten JL, de Wijkerslooth LR, Leenders M, et al. Variation in palliative care of esophageal cancer in clinical practice: factors associated with treatment decisions. Dis Esophagus 2017;30:1-7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
