Narrative review of the management of oral mucositis during chemoradiation for head and neck cancer
- PMID: 34164550
- PMCID: PMC8184418
- DOI: 10.21037/atm-20-3931
Narrative review of the management of oral mucositis during chemoradiation for head and neck cancer
Abstract
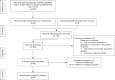
Oral mucositis (OM) can be a significant problem for patients undergoing radiation or chemoradiation for head and neck cancer. In modern clinical trials, grade 3-4 OM can be seen in over 40% of patients and can cause a significant impact on their quality of life (QOL). Despite this fact, strategies for the prevention and treatment of OM vary widely, with options including both lifestyle modifications and pharmaceuticals. Here we evaluate and summarize the current clinical interventions for the management of radiation-induced OM. The majority of the current evidence focuses on reducing OM related pain. These agents are detailed over multiple clinical trials including treatment modalities such as: GC4419, doxepin mouthwash, diphenhydramine-lidocaine-antacid (DLA) mouthwash, gabapentin, and methadone. While several strategies have been employed to prevent radiation-induced OM, there is currently no strong evidence for the routine use of these agents in the clinic. After summarization of these treatments, we offer practical guidance for the treatment of OM in the clinic. We recommend a multiagent approach of pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatments including oral rinses, home humidification, escalating doses of gabapentin, doxepin or DLA mouthwash, over the counter analgesics, and lastly methadone. These interventions are tailored to address the expected increase of severity of symptoms during the course of head and neck radiotherapy.
Keywords: Head and Neck Cancer; Radiation therapy; oral mucositis (OM).
2021 Annals of Translational Medicine. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/atm-20-3931). The series “Head and Neck Cancers – Disease Biology, Diagnostics, Prevention and Management” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- McCloskey SA, Jaggernauth W, Rigual NR, et al. Radiation treatment interruptions greater than one week and low hemoglobin levels (12 g/dL) are predictors of local regional failure after definitive concurrent chemotherapy and intensity-modulated radiation therapy for squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Am J Clin Oncol 2009;32:587-91. 10.1097/COC.0b013e3181967dd0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources