METTL3/N6-methyladenosine/ miR-21-5p promotes obstructive renal fibrosis by regulating inflammation through SPRY1/ERK/NF-κB pathway activation
- PMID: 34164910
- PMCID: PMC8358893
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16603
METTL3/N6-methyladenosine/ miR-21-5p promotes obstructive renal fibrosis by regulating inflammation through SPRY1/ERK/NF-κB pathway activation
Abstract
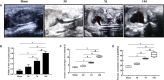
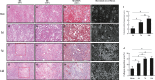
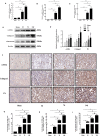
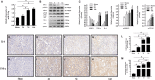
Renal fibrosis induced by urinary tract obstruction is a common clinical occurrence; however, effective treatment is lacking, and a deeper understanding of the mechanism of renal fibrosis is needed. Previous studies have revealed that miR-21 impacts liver and lung fibrosis progression by activating the SPRY1/ERK/NF-kB signalling pathway. However, whether miR-21 mediates obstructive renal fibrosis through the same signalling pathway has not been determined. Additionally, studies have shown that N6-methyladenosine (m6 A) modification-dependent primary microRNA (pri-microRNA) processing is essential for maturation of microRNAs, but its role in the maturation of miR-21 in obstructive renal fibrosis has not yet been investigated in detail. To address these issues, we employed a mouse model of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) in which the left ureters were ligated for 3, 7 and 14 days to simulate the fibrotic process. In vitro, human renal proximal tubular epithelial (HK-2) cells were transfected with plasmids containing the corresponding sequence of METTL3, miR-21-5p mimic or miR-21-5p inhibitor. We found that the levels of miR-21-5p and m6 A modification in the UUO model groups increased significantly, and as predicted, the SPRY1/ERK/NF-kB pathway was activated by miR-21-5p, confirming that miR-21-5p plays an important role in obstructive renal fibrosis by enhancing inflammation. METTL3 was found to play a major catalytic role in m6 A modification in UUO mice and drove obstructive renal fibrosis development by promoting miR-21-5p maturation. Our research is the first to demonstrate the role of the METTL3-m6 A-miR-21-5p-SPRY1/ERK/NF-kB axis in obstructive renal fibrosis and provides a deeper understanding of renal fibrosis.
Keywords: METTL3; N6-methyladenosine (m6A); Spry1/ERK/NF-κB; miR-21-5p; renal fibrosis; urinary tract obstruction.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MiR-9-5p protects from kidney fibrosis by metabolic reprogramming.FASEB J. 2020 Jan;34(1):410-431. doi: 10.1096/fj.201901599RR. Epub 2019 Nov 22. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 31914684
-
METTL3 aggravates renal fibrogenesis in obstructive nephropathy via the miR-199a-3p/PAR4 axis.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 5;982:176931. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176931. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39182553
-
Mechanistic study on lncRNA XIST/miR-124-3p/ITGB1 axis in renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy.Exp Cell Res. 2024 Sep 1;442(1):114194. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.114194. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Exp Cell Res. 2024. PMID: 39127440
-
Mediators of fibrosis and apoptosis in obstructive uropathies.Curr Urol Rep. 2005 Mar;6(2):140-5. doi: 10.1007/s11934-005-0083-5. Curr Urol Rep. 2005. PMID: 15717973 Review.
-
Methyltransferase-like 3 represents a prospective target for the diagnosis and treatment of kidney diseases.Hum Genomics. 2024 Nov 14;18(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s40246-024-00692-8. Hum Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39538346 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling pathways of chronic kidney diseases, implications for therapeutics.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jun 9;7(1):182. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01036-5. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35680856 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integration of multi-omics summary data reveals the role of N6-methyladenosine in neuropsychiatric disorders.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Oct;29(10):3141-3150. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02574-w. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38684796
-
The role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation modification in kidney diseases: from mechanism to therapeutic potential.PeerJ. 2025 Aug 27;13:e19940. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19940. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40895041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNA-Mediated Epigenetic Regulation in Hepatic Stellate Cells of Liver Fibrosis.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Aug 7;10(4):44. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10040044. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 39195573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
N6-methyladenine RNA Methylation Epigenetic Modification and Kidney Diseases.Kidney Int Rep. 2022 Oct 17;8(1):36-50. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.10.009. eCollection 2023 Jan. Kidney Int Rep. 2022. PMID: 36644366 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu L, Wang Y, Yan R, et al. BMP‐7 inhibits renal fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy via miR‐21 downregulation. Life Sci. 2019;238:116957. - PubMed
-
- Lyu H, Li X, Wu Q, Hao L. Overexpression of microRNA‐21 mediates Ang II‐induced renal fibrosis by activating the TGF‐beta1/Smad3 pathway via suppressing PPARalpha. J Pharmacol Sci. 2019;141:70‐78. - PubMed
-
- Tang CR, Luo SG, Lin X, et al. Silenced miR‐21 inhibits renal interstitial fibrosis via targeting ERK1/2 signaling pathway in mice. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23:110‐116. - PubMed
-
- Zhou TB, Jiang ZP. Role of miR‐21 and its signaling pathways in renal diseases. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2014;34:335‐337. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

