A Novel 29-Messenger RNA Host-Response Assay From Whole Blood Accurately Identifies Bacterial and Viral Infections in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Suspected Infections: A Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 34166284
- PMCID: PMC8439671
- DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005119
A Novel 29-Messenger RNA Host-Response Assay From Whole Blood Accurately Identifies Bacterial and Viral Infections in Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Suspected Infections: A Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
Objectives: The rapid diagnosis of acute infections and sepsis remains a serious challenge. As a result of limitations in current diagnostics, guidelines recommend early antimicrobials for suspected sepsis patients to improve outcomes at a cost to antimicrobial stewardship. We aimed to develop and prospectively validate a new, 29-messenger RNA blood-based host-response classifier Inflammatix Bacterial Viral Non-Infected version 2 (IMX-BVN-2) to determine the likelihood of bacterial and viral infections.
Design: Prospective observational study.
Setting: Emergency Department, Campus Benjamin Franklin, Charité-Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Germany.
Patients: Three hundred twelve adult patients presenting to the emergency department with suspected acute infections or sepsis with at least one vital sign change.
Interventions: None (observational study only).
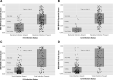
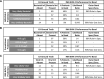
Measurements and main results: Gene expression levels from extracted whole blood RNA was quantified on a NanoString nCounter SPRINT (NanoString Technologies, Seattle, WA). Two predicted probability scores for the presence of bacterial and viral infection were calculated using the IMX-BVN-2 neural network classifier, which was trained on an independent development set. The IMX-BVN-2 bacterial score showed an area under the receiver operating curve for adjudicated bacterial versus ruled out bacterial infection of 0.90 (95% CI, 0.85-0.95) compared with 0.89 (95% CI, 0.84-0.94) for procalcitonin with procalcitonin being used in the adjudication. The IMX-BVN-2 viral score area under the receiver operating curve for adjudicated versus ruled out viral infection was 0.83 (95% CI, 0.77-0.89).
Conclusions: IMX-BVN-2 demonstrated accuracy for detecting both viral infections and bacterial infections. This shows the potential of host-response tests as a novel and practical approach for determining the causes of infections, which could improve patient outcomes while upholding antimicrobial stewardship.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Society of Critical Care Medicine and Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Drs. Bauer’s, Kappert’s, Galtung’s, Lehmann’s, Tauber’s, and Somasundaram’s institution received funding from Inflammatix and Gentian AS. Dr. Kappert’s and Tauber’s institution received funding from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Stiftung für Pathobiochemie und Molekulare Diagnostik, and Deutsche Stiftung Innere Medizin. Drs. Wacker, Liesenfeld, Buturovic, Cheng, Sweeney, and Luethy disclosed that they are employees of and option shareholders in Inflammatix.
Figures
Comment in
-
A Host of Host Assays: The Clinical Accuracy of Two Host Gene Expression Assays in Acute Infection.Crit Care Med. 2021 Oct 1;49(10):1812-1814. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005220. Crit Care Med. 2021. PMID: 34529611 No abstract available.
References
-
- Álvaro-Meca A, Jiménez-Sousa MA, Micheloud D, et al. ; Group of Biomedical Research in Critical Care Medicine (BioCritic): Epidemiological trends of sepsis in the twenty-first century (2000-2013): An analysis of incidence, mortality, and associated costs in Spain. Popul Health Metr. 2018; 16:4. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, et al. : Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Crit Care Med. 2017; 45:486–552 - PubMed
-
- Sweeney TE, Liesenfeld O, May L: Diagnosis of bacterial sepsis: Why are tests for bacteremia not sufficient? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2019; 19:959–962 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

