Diagnostic accuracy of Panbio rapid antigen tests on oropharyngeal swabs for detection of SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 34166410
- PMCID: PMC8224876
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253321
Diagnostic accuracy of Panbio rapid antigen tests on oropharyngeal swabs for detection of SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
Background: Antigen-detecting rapid diagnostic tests (Ag-RDTs) for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 offer new opportunities for testing in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic. Nasopharyngeal swabs (NPS) are the reference sample type, but oropharyngeal swabs (OPS) may be a more acceptable sample type in some patients.
Methods: We conducted a prospective study in a single screening center to assess the diagnostic performance of the Panbio™ COVID-19 Ag Rapid Test (Abbott) on OPS compared with reverse-transcription quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) using NPS during the second pandemic wave in Switzerland.
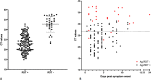
Results: 402 outpatients were enrolled in a COVID-19 screening center, of whom 168 (41.8%) had a positive RT-qPCR test. The oropharyngeal Ag-RDT clinical sensitivity compared to nasopharyngeal RT-qPCR was 81% (95%CI: 74.2-86.6). Two false positives were noted out of the 234 RT-qPCR negative individuals, which resulted in a clinical specificity of 99.1% (95%CI: 96.9-99.9) for the Ag-RDT. For cycle threshold values ≤ 26.7 (≥ 1E6 SARS-CoV-2 genomes copies/mL, a presumed cut-off for infectious virus), 96.3% sensitivity (95%CI: 90.7-99.0%) was obtained with the Ag-RDT using OPS.
Interpretation: Based on our findings, the diagnostic performance of the Panbio™ Covid-19 RDT with OPS samples, if taken by a trained person and high requirements regarding quality of the specimen, meet the criteria required by the WHO for Ag-RDTs (sensitivity ≥80% and specificity ≥97%) in a high incidence setting in symptomatic individuals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Nov 30]. https://covid19.who.int
-
- COVID-19 Target product profiles for priority diagnostics to support response to the COVID-19 pandemic v.1.0 [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2020 Oct 8]. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/covid-19-target-product-profiles...
-
- Berger A, Nsoga MTN, Perez-Rodriguez FJ, Aad YA, Sattonnet-Roche P, Gayet-Ageron A, et al.. Diagnostic accuracy of two commercial SARS-CoV-2 antigen-detecting rapid tests at the point of care in community-based testing centers. PLOS ONE. 2021. Mar 31;16(3):e0248921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248921 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Linares M, Pérez-Tanoira R, Carrero A, Romanyk J, Pérez-García F, Gómez-Herruz P, et al.. Panbio antigen rapid test is reliable to diagnose SARS-CoV-2 infection in the first 7 days after the onset of symptoms. Journal of Clinical Virology. 2020. Oct 16;104659. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104659 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

