First-Dose mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Allergic Reactions: Limited Role for Excipient Skin Testing
- PMID: 34166844
- PMCID: PMC8217699
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.06.010
First-Dose mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Allergic Reactions: Limited Role for Excipient Skin Testing
Abstract
Background: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention state that a severe or immediate allergic reaction to the first dose of an mRNA COVID-19 vaccine is a contraindication for the second dose.
Objective: To assess outcomes associated with excipient skin testing after a reported allergic reaction to the first dose of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine.
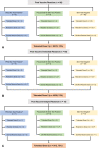
Methods: We identified a consecutive sample of patients with reported allergic reactions after the first dose of mRNA COVID-19 vaccine who underwent allergy assessment with skin testing to polyethylene glycol (PEG) and, when appropriate, polysorbate 80. Skin testing results in conjunction with clinical phenotyping of the first-dose mRNA COVID-19 vaccine reaction guided second-dose vaccination recommendation. Second-dose mRNA COVID-19 vaccine reactions were assessed.
Results: Eighty patients with reported first-dose mRNA COVID-19 vaccine allergic reactions (n = 65; 81% immediate onset) underwent excipient skin testing. Of those, 14 (18%) had positive skin tests to PEG (n = 5) and/or polysorbate 80 (n = 12). Skin testing result did not affect tolerance of the second dose in patients with immediate or delayed reactions. Of the 70 patients who received the second mRNA COVID-19 vaccine dose (88%), 62 had either no reaction or a mild reaction managed with antihistamines (89%), but 2 patients required epinephrine treatment. Three patients with positive PEG-3350 intradermal (methylprednisolone) testing tolerated second-dose mRNA COVID-19 vaccination. Refresh Tears caused nonspecific skin irritation.
Conclusions: Most individuals with a reported allergic reaction to the first dose of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, regardless of skin test result, received the second dose safely. More data are needed on the value of skin prick testing to PEG (MiraLAX) in evaluating patients with mRNA COVID-19 vaccine anaphylaxis. Refresh Tears should not be used for skin testing.
Keywords: Anaphylaxis; COVID-19; COVID-19 vaccine; Drug allergy; Excipient allergy; PEG allergy; Polysorbate allergy; Skin testing; Vaccine allergy.
Copyright © 2021 American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
PEG/Polysorbate Skin Testing Has No Utility in the Assessment of Suspected Allergic Reactions to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 Sep;9(9):3321-3322. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.06.025. Epub 2021 Jul 31. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021. PMID: 34393075 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center COVID-19 map. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html Available from:
-
- US Food and Drug Administration Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. https://www.fda.gov/emergency-preparedness-and-response/coronavirus-dise... Available from:
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention COVID-19 vaccines for people with allergies. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/speci... Available from: - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention What to do if you have an allergic reaction after getting a COVID-19 vaccine. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/safety/allergic-react... Available from:
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

