Acute myocarditis after a second dose of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine: a report of two cases
- PMID: 34166884
- PMCID: PMC8216670
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2021.06.019
Acute myocarditis after a second dose of the mRNA COVID-19 vaccine: a report of two cases
Abstract
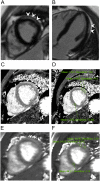
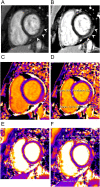
We report two cases of myocarditis, in two young and previously healthy individuals, temporally related to the second dose of the mRNA-COVID-19 vaccine. Both patients developed acute chest pain, changes on electrocardiogram (ECG), and elevated serum troponin within two days of receiving their second dose. Cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) findings were consistent with acute myocarditis.
Keywords: Acute myocarditis; COVID-19 vaccination; Cardiac magnetic resonance; Myocarditis; mRNA-COVID-19 vaccine.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Yamamoto H., Hashimoto T., Ohta-Ogo K., et al. A case of biopsy-proven eosinophilic myocarditis related to tetanus toxoid immunization. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2018;37:54–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

