Microwave ablation compared with radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 34167181
- PMCID: PMC8366737
- DOI: 10.2478/raon-2021-0030
Microwave ablation compared with radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of liver cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Guidelines have reported that although microwave ablation (MWA) has potential advantages over radiofrequency ablation (RFA), superiority in efficacy and safety remain unclear. Aim of the study is to compare MWA with RFA in the treatment of liver cancer.
Methods: Meta-analysis was conducted according to the PRISMA guidelines for studies published from 2010 onwards. A random-effects model was used for the meta-analyses. Complete ablation (CA), local tumor progression (LTP), intrahepatic distant recurrence (IDR), and complications were analyzed.
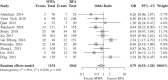
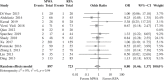
Results: Four randomized trials and 11 observational studies with a total of 2,169 patients met the inclusion criteria. Although overall analysis showed no significant difference in LTP between MWA and RFA, subgroup analysis including randomized trials for patients with hepatocellular cancer (HCC) demonstrated statistically decreased rates of LTP in favor of MWA (OR, 0.40; 95% CI, 0.18-0.92; p = 0.03). No significant differences were found between the two procedures in CA, IDR, complications, and tumor diameter less or larger than 3 cm.
Conclusions: MWA showed promising results and demonstrated better oncological outcomes in terms of LTP compared to RFA in patients with HCC. MWA can be utilized as the ablation method of choice in patients with HCC.
Keywords: carcinoma hepatocellular; liver; liver neoplasms; microwaves; radiofrequency ablation.
© 2021 Antonios E. Spiliotis, Gereon Gäbelein, Sebastian Holländer, Philipp-Robert Scherber, Matthias Glanemann, Bijendra Patel, published by Sciendo.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Comparison of Microwave and Radiofrequency Ablation for the Treatment of Small- and Medium-Sized Hepatocellular Carcinomas in a Prospective Randomized Trial.Rofo. 2024 May;196(5):482-490. doi: 10.1055/a-2203-2733. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Rofo. 2024. PMID: 38065541 Clinical Trial. English.
-
Efficacy of microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score analysis.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Aug;46(8):3790-3797. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03008-9. Epub 2021 Mar 6. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021. PMID: 33675382 Free PMC article.
-
Small single perivascular hepatocellular carcinoma: comparisons of radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation by using propensity score analysis.Eur Radiol. 2021 Jul;31(7):4764-4773. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07571-5. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Eur Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33399908 Free PMC article.
-
Radiofrequency ablation versus microwave ablation for early stage hepatocellular carcinoma: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Oct 23;99(43):e22703. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022703. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33120763 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous thermal ablation for primary hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Feb;31(2):294-301. doi: 10.1111/jgh.13028. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26114968
Cited by
-
Ultrasound-Guided Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Hepatic Focal Nodular Hyperplasia--A Multicenter Retrospective Study.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jan 6;9:826926. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.826926. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35071222 Free PMC article.
-
[Irreversible electroporation: present and future in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma].An Sist Sanit Navar. 2022 Nov 21;45(3):e1019. doi: 10.23938/ASSN.1019. An Sist Sanit Navar. 2022. PMID: 36413004 Free PMC article. Review. Spanish.
-
Efficacy and safety of ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma at specific anatomic sites of the liver: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2025 Jul 7;25(1):505. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-04081-w. BMC Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40624629 Free PMC article.
-
The microbiological features and risk factors for liver abscess after thermal ablation of liver cancer.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025 Jun 6;15:1567105. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1567105. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40546284 Free PMC article.
-
Liver-Directed Therapy for Neuroendocrine Metastases: From Interventional Radiology to Nuclear Medicine Procedures.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Dec 19;13(24):6368. doi: 10.3390/cancers13246368. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34944988 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Glassberg MB, Ghosh S, Clymer JW, Wright GWJ, Ferko N, Amaral JF. Microwave ablation compared with hepatic resection for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Surg Oncol. 2019;17:98. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1632-6. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
