Integrative Multi-Omics Reveals Serum Markers of Tuberculosis in Advanced HIV
- PMID: 34168648
- PMCID: PMC8217878
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.676980
Integrative Multi-Omics Reveals Serum Markers of Tuberculosis in Advanced HIV
Abstract
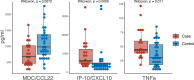
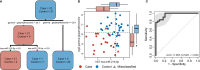
Tuberculosis (TB) accounts for disproportionate morbidity and mortality among persons living with HIV (PLWH). Conventional methods of TB diagnosis, including smear microscopy and Xpert MTB/RIF, have lower sensitivity in PLWH. Novel high-throughput approaches, such as miRNAomics and metabolomics, may advance our ability to recognize subclinical and difficult-to-diagnose TB, especially in very advanced HIV. We conducted a case-control study leveraging REMEMBER, a multi-country, open-label randomized controlled trial comparing 4-drug empiric standard TB treatment with isoniazid preventive therapy in PLWH initiating antiretroviral therapy (ART) with CD4 cell counts <50 cells/μL. Twenty-three cases of incident TB were site-matched with 32 controls to identify microRNAs (miRNAs), metabolites, and cytokines/chemokines, associated with the development of newly diagnosed TB in PLWH. Differentially expressed miRNA analysis revealed 11 altered miRNAs with a fold change higher than 1.4 or lower than -1.4 in cases relative to controls (p<0.05). Our analysis revealed no differentially abundant metabolites between cases and controls. We found higher TNFα and IP-10/CXCL10 in cases (p=0.011, p=0.0005), and higher MDC/CCL22 in controls (p=0.0072). A decision-tree algorithm identified gamma-glutamylthreonine and hsa-miR-215-5p as the optimal variables to classify incident TB cases (AUC 0.965; 95% CI 0.925-1.000). hsa-miR-215-5p, which targets genes in the TGF-β signaling pathway, was downregulated in cases. Gamma-glutamylthreonine, a breakdown product of protein catabolism, was less abundant in cases. To our knowledge, this is one of the first uses of a multi-omics approach to identify incident TB in severely immunosuppressed PLWH.
Keywords: HIV; biomarker; metabolomics; microRNA; multi-omics; tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2021 Krishnan, Queiroz, Gupta, Gupte, Bisson, Kumwenda, Naidoo, Mohapi, Mave, Mngqibisa, Lama, Hosseinipour, Andrade and Karakousis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor declared a past co-authorship with one of the authors NK.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Global Tuberculosis Report 2020. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2020). Available at: http://library1.nida.ac.th/termpaper6/sd/2554/19755.pdf.
-
- Horne D, Kohli M, Zifodya J, Schiller I, Dendukuri N, Tollefson D, et al. . Xpert MTB/RIF and Xpert MTB/RIF Ultra for Pulmonary Tuberculosis and Rifampicin Resistance in Adults (Review). Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2019) 6:1–276. 10.1002/14651858.CD009593.pub4.www.cochranelibrary.com - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

