Mechanisms linking gut microbial metabolites to insulin resistance
- PMID: 34168724
- PMCID: PMC8192250
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i6.730
Mechanisms linking gut microbial metabolites to insulin resistance
Abstract
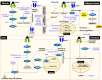
Insulin resistance is the rate-limiting step in the development of metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes. The gut microbiota has been implicated in host energy metabolism and metabolic diseases and is recognized as a quantitatively important organelle in host metabolism, as the human gut harbors 10 trillion bacterial cells. Gut microbiota break down various nutrients and produce metabolites that play fundamental roles in host metabolism and aid in the identification of possible therapeutic targets for metabolic diseases. Therefore, understanding the various effects of bacterial metabolites in the development of insulin resistance is critical. Here, we review the mechanisms linking gut microbial metabolites to insulin resistance in various insulin-responsive tissues.
Keywords: Adipose tissue; Gut bacterial metabolites; Insulin resistance; Intestine; Liver; Skeletal muscle.
©The Author(s) 2021. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gesta S, Tseng YH, Kahn CR. Developmental origin of fat: tracking obesity to its source. Cell. 2007;131:242–256. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

