Identification of a Locus on the X Chromosome Linked to Familial Membranous Nephropathy
- PMID: 34169208
- PMCID: PMC8207324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.02.025
Identification of a Locus on the X Chromosome Linked to Familial Membranous Nephropathy
Abstract
Introduction: Membranous nephropathy (MN) is the most common cause of nephrotic syndrome (NS) in adults and is a leading cause of end-stage renal disease due to glomerulonephritis. Primary MN has a strong male predominance, accounting for approximately 65% of cases; yet, currently associated genetic loci are all located on autosomes. Previous reports of familial MN have suggested the existence of a potential X-linked susceptibility locus. Identification of such risk locus may provide clues to the etiology of MN.
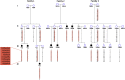
Methods: We identified 3 families with 8 members affected by primary MN. Genotyping was performed using single-nucleotide polymorphism microarrays, and serum was sent for anti-phospholipase A2 receptor (PLA2R) antibody testing. All affected members were male and connected through the maternal line, consistent with X-linked inheritance. Genome-wide multipoint parametric linkage analysis using a model of X-linked recessive inheritance was conducted, and genetic risk scores (GRSs) based on known MN-associated variants were determined.
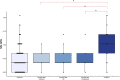
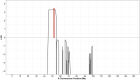
Results: Anti-PLA2R testing was negative in all affected family members. Linkage analysis revealed a significant logarithm of the odds score (3.260) on the short arm of the X chromosome at a locus of approximately 11 megabases (Mb). Haplotype reconstruction further uncovered a shared haplotype spanning 2 Mb present in all affected individuals from the 3 families. GRSs in familial MN were significantly lower than in anti-PLA2R-associated MN and were not different from controls.
Conclusions: Our study identifies linkage of familial membranous nephropathy to chromosome Xp11.3-11.22. Family members affected with MN have a significantly lower GRS than individuals with anti-PLA2R-associated MN, suggesting that X-linked familial MN represents a separate etiologic entity.
Keywords: LOD score; X-linked; genetic risk score; glomerulonephritis; linkage analysis; membranous nephropathy.
© 2021 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Couser W.G., Cattran D.C. Chapter 20: Membranous Nephropathy. In: Floege J., Johnson R.J., Feehall J., editors. Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology. Fourth Ed. Elsevier, Amsterdam; The Netherlands: 2010. pp. 248–259.
-
- Ronco P., Debiec H., Gulati S. Chapter 20: Membranous Nephropathy. In: Geary D.F., Schaefer F., editors. Pediatric Kidney Disease. Second Edition. Springer-Verlag; Berlin, Heidelberg: 2016. pp. 529–546.
-
- Bockenhauer D., Debiec H., Sebire N. Familial membranous nephropathy: an X-linked genetic susceptibility? Nephron Clin Pract. 2008;108:c10–c15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

