Changes in Central Corneal Thickness With Air-Puff-Induced Corneal Deformation Using a Method to Correct Scheimpflug and Refractive Distortion
- PMID: 34170774
- PMCID: PMC8957395
- DOI: 10.3928/1081597X-20210219-01
Changes in Central Corneal Thickness With Air-Puff-Induced Corneal Deformation Using a Method to Correct Scheimpflug and Refractive Distortion
Abstract
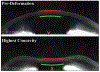
Purpose: To establish a method to determine central corneal thickness (CCT) and anterior chamber depth (ACD) of an air-puff-deformed cornea at the highest concavity (HC) state.
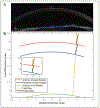
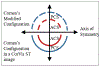
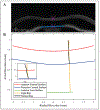
Methods: The Fink method for refractive correction of Scheimpflug images of a convex pre-deformed (PRE) cornea was implemented for 155 eyes of 155 participants imaged with the Corvis ST (Oculus Optikgeräte GmbH). This method was subsequently modified for the HC state of deformation. The tracked edges of each participant's cornea were exported at the PRE and HC states. Ten participants who had a visible crystalline lens in the image were selected to determine ACD in both states. The center points on the corneal tracked edges and lens were used to determine uncorrected CCT and ACD, respectively.
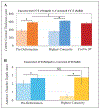
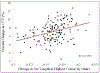
Results: Average undeformed CCTPRE was significantly lower than deformed CCTHC (584 ± 31 and 626 ± 34 µm, respectively) (P < .0001). No significant difference was found for the corrected ACD between the two states. Corrected CCT and ACD were significantly greater than the corresponding uncorrected values for both deformation states (P < .0001). Percent change in CCT was found to be correlated to change in arc length at HC (P < .0001).
Conclusions: Distortion in Corvis ST images at the HC state can be corrected using a modified Fink method. CCT was found to increase in the HC state, compared to the PRE state. The CCT change during deformation may be important in the study of the compressive response of the cornea. [J Refract Surg. 2021;37(6):422-428.].
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: Dr. Roberts is a consultant to Oculus Optikgeräte GmbH, Zeimer Ophthalmic Systems AG, and Optimo Medical. The remaining authors have no financial or proprietary interest in the materials presented herein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Influence factors and differences of posterior corneal elevation measured by Pentacam system combined with Corvis ST].Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2020 Feb 11;56(2):110-117. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0412-4081.2020.02.006. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32074821 Chinese.
-
Introduction of Two Novel Stiffness Parameters and Interpretation of Air Puff-Induced Biomechanical Deformation Parameters With a Dynamic Scheimpflug Analyzer.J Refract Surg. 2017 Apr 1;33(4):266-273. doi: 10.3928/1081597X-20161221-03. J Refract Surg. 2017. PMID: 28407167
-
Intraocular pressure measurements and corneal biomechanical properties using a dynamic Scheimpflug analyzer, after several keratoplasty techniques, versus normal eyes.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2018 Jan;41(1):30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2017.06.006. Epub 2017 Nov 28. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2018. PMID: 29191679
-
In vivo human corneal deformation analysis with a Scheimpflug camera, a critical review.J Biophotonics. 2016 May;9(5):464-77. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201500233. Epub 2016 Feb 12. J Biophotonics. 2016. PMID: 26871552 Review.
-
Human corneal thickness and its impact on intraocular pressure measures: a review and meta-analysis approach.Surv Ophthalmol. 2000 Mar-Apr;44(5):367-408. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6257(00)00110-7. Surv Ophthalmol. 2000. PMID: 10734239 Review.
Cited by
-
A New Biomechanical Deformation Response Parameter: Change in Central Corneal Thickness During Air Puff Induced Corneal Deformation.Curr Eye Res. 2024 Aug;49(8):798-802. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2024.2338228. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Curr Eye Res. 2024. PMID: 38629736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reisdorf S Measuring biomechanical properties in vivo: the Corvis® ST. In: Roberts CJ, Liu J, eds. Corneal Biomechanics: From Theory to Practice. Kugler Publications; 2017:91.
-
- Lee H, Roberts CJ, Ambrósio R, Elsheikh A, Kang DSY, Kim T. Effect of accelerated corneal crosslinking combined with transepithelial photorefractive keratectomy on dynamic corneal response parameters and biomechanically corrected intraocular pressure measured with a dynamic scheimpflug analyzer in healthy myopic patient. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2017;43(7):937–945. doi:10.1016/j.jcrs.2017.04.036 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

