BAP1/ASXL complex modulation regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition during trophoblast differentiation and invasion
- PMID: 34170818
- PMCID: PMC8233037
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.63254
BAP1/ASXL complex modulation regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition during trophoblast differentiation and invasion
Abstract
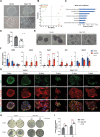
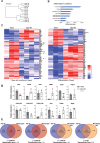
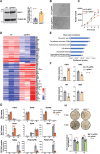
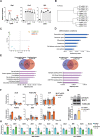
Normal function of the placenta depends on the earliest developmental stages when trophoblast cells differentiate and invade into the endometrium to establish the definitive maternal-fetal interface. Previously, we identified the ubiquitously expressed tumour suppressor BRCA1-associated protein 1 (BAP1) as a central factor of a novel molecular node controlling early mouse placentation. However, functional insights into how BAP1 regulates trophoblast biology are still missing. Using CRISPR/Cas9 knockout and overexpression technology in mouse trophoblast stem cells, here we demonstrate that the downregulation of BAP1 protein is essential to trigger epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during trophoblast differentiation associated with a gain of invasiveness. Moreover, we show that the function of BAP1 in suppressing EMT progression is dependent on the binding of BAP1 to additional sex comb-like (ASXL1/2) proteins to form the polycomb repressive deubiquitinase (PR-DUB) complex. Finally, both endogenous expression patterns and BAP1 overexpression experiments in human trophoblast stem cells suggest that the molecular function of BAP1 in regulating trophoblast differentiation and EMT progression is conserved in mice and humans. Our results reveal that the physiological modulation of BAP1 determines the invasive properties of the trophoblast, delineating a new role of the BAP1 PR-DUB complex in regulating early placentation.
Keywords: CRISPR gene editing; developmental biology; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; human; mouse; placenta; regenerative medicine; stem cell self-renewal; stem cells; trophoblast; trophoblast invasion.
© 2021, Perez-Garcia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
VP, GL, PL, HO, GB, AM, MT, MH No competing interests declared
Figures
Similar articles
-
Understanding the intersection between placental development and cancer: Lessons from the tumor suppressor BAP1.Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 27;7(1):1053. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06689-2. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39191942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The BAP1/ASXL2 Histone H2A Deubiquitinase Complex Regulates Cell Proliferation and Is Disrupted in Cancer.J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 27;290(48):28643-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.661553. Epub 2015 Sep 28. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26416890 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of histone H2A lysine 119 deubiquitination by Polycomb repressive deubiquitinase BAP1/ASXL1.Sci Adv. 2023 Aug 9;9(32):eadg9832. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg9832. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37556531 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-derived neomorphic mutations in ASXL1 impairs the BAP1-ASXL1-FOXK1/K2 transcription network.Protein Cell. 2021 Jul;12(7):557-577. doi: 10.1007/s13238-020-00754-2. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Protein Cell. 2021. PMID: 32683582 Free PMC article.
-
The ASXL-BAP1 axis: new factors in myelopoiesis, cancer and epigenetics.Leukemia. 2013 Jan;27(1):10-5. doi: 10.1038/leu.2012.288. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Leukemia. 2013. PMID: 23147254 Review.
Cited by
-
BAP1 controls mesenchymal stem cell migration by inhibiting the ERK signaling pathway.BMB Rep. 2024 May;57(5):250-255. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2023-0174. BMB Rep. 2024. PMID: 37964637 Free PMC article.
-
The GPI-anchor biosynthesis pathway is critical for syncytiotrophoblast differentiation and placental development.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 May 31;81(1):246. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05284-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 38819479 Free PMC article.
-
Fetal growth restriction and placental defects in obese mice are associated with impaired decidualisation: the role of increased leptin signalling modulators SOCS3 and PTPN2.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Aug 1;81(1):329. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05336-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39090270 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding the intersection between placental development and cancer: Lessons from the tumor suppressor BAP1.Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 27;7(1):1053. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06689-2. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39191942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Underlying Molecular Mechanisms of the Placenta Accreta Spectrum: A Narrative Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 8;25(17):9722. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179722. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273667 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdel-Wahab O, Adli M, LaFave LM, Gao J, Hricik T, Shih AH, Pandey S, Patel JP, Chung YR, Koche R, Perna F, Zhao X, Taylor JE, Park CY, Carroll M, Melnick A, Nimer SD, Jaffe JD, Aifantis I, Bernstein BE, Levine RL. ASXL1 mutations promote myeloid transformation through loss of PRC2-mediated gene repression. Cancer Cell. 2012;22:180–193. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.06.032. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

