Design, development and optimization of sustained release floating, bioadhesive and swellable matrix tablet of ranitidine hydrochloride
- PMID: 34170952
- PMCID: PMC8232414
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253391
Design, development and optimization of sustained release floating, bioadhesive and swellable matrix tablet of ranitidine hydrochloride
Abstract
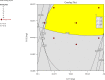
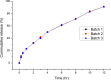
Ranitidine HCl, a selective, competitive histamine H2-receptor antagonist with a short biological half-life, low bioavailability and narrow absorption window, is an ideal candidate for gastro-retentive drug delivery system (GRDDS). Controlled release with an optimum retentive formulation in the upper stomach would be an ideal formulation for this drug. The aim of the present study was therefore to develop, formulate and optimize floating, bioadhesive, and swellable matrix tablets of ranitidine HCl. The matrix tablets were prepared using a combination of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (NaCMC) as release retarding polymers, sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) as gas generating agent and microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) as direct compression diluent. Central composite design (CCD) was used to optimize the formulation and a total of thirteen formulations were prepared. Concentration of HPMC/NaCMC (3:1) (X1) and NaHCO3 (X2) were selected as independent variables; and floating lag time (Y1), bioadhesive strength (Y2), swelling index at 12 h (Y3), cumulative drug release at 1 h (Y4), time to 50% drug release (t50%) (Y5) and cumulative drug release at 12 h (Y6) were taken as the response variables. The optimized batch showed floating lag time of 5.09 sec, bioadhesive strength of 29.69 g, swelling index of 315.04% at 12 h, t50% of 3.86 h and drug release of 24.21% and 93.65% at 1h and 12 h, respectively, with anomalous release mechanism. The results indicate that sustained release matrix tablet of ranitidine HCl with combined floating, bioadhesive and swelling gastro-retentive properties can be considered as a strategy to overcome the low bioavailability and in vivo variation associated with the conventional ranitidine HCl tablet.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Kanupriya C, Nimrata S, Gill NS. Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System: a Significant Tool To Increase the Gastric Residence Time of Drugs. Int J Curr Pharm Res. 2021;13: 7–11.
-
- Alluri R, Sai A, Aeila S, Sai TM. Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System-An Overview. World J Pharm Sci. 2020; 9: 481–490.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

