Profiling SARS-CoV-2 HLA-I peptidome reveals T cell epitopes from out-of-frame ORFs
- PMID: 34171305
- PMCID: PMC8173604
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.046
Profiling SARS-CoV-2 HLA-I peptidome reveals T cell epitopes from out-of-frame ORFs
Abstract
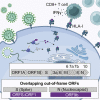
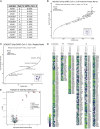
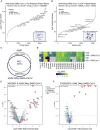
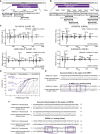
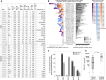
T cell-mediated immunity plays an important role in controlling SARS-CoV-2 infection, but the repertoire of naturally processed and presented viral epitopes on class I human leukocyte antigen (HLA-I) remains uncharacterized. Here, we report the first HLA-I immunopeptidome of SARS-CoV-2 in two cell lines at different times post infection using mass spectrometry. We found HLA-I peptides derived not only from canonical open reading frames (ORFs) but also from internal out-of-frame ORFs in spike and nucleocapsid not captured by current vaccines. Some peptides from out-of-frame ORFs elicited T cell responses in a humanized mouse model and individuals with COVID-19 that exceeded responses to canonical peptides, including some of the strongest epitopes reported to date. Whole-proteome analysis of infected cells revealed that early expressed viral proteins contribute more to HLA-I presentation and immunogenicity. These biological insights, as well as the discovery of out-of-frame ORF epitopes, will facilitate selection of peptides for immune monitoring and vaccine development.
Keywords: HLA Class I; SARS-CoV-2; T Cell response; coronavirus; immunogenicity; out-of-frame ORF immunopeptidomics; viral infection.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.W.-G., S.K., S.S., K.R.C, N.H., S.A.C., J.G.A., M.S., and P.C.S. are named co-inventors on a patent application related to immunogenic compositions of this manuscript filed by The Broad Institute that is being made available in accordance with the COVID-19 technology licensing framework to maximize access to university innovations. D.L.-E., C.T., Y.W., M.R.D., W.A.D., and D.C.P. are employees and stockholders of Repertoire Immune Medicines. N.B. is an extramural member of the Parker Institute for Cancer Immunotherapy; receives research funds from Regeneron, Harbor Biomedical, DC Prime, and Dragonfly Therapeutics; and is on the advisory boards of Neon Therapeutics, Novartis, Avidea, Boehringer Ingelheim, Rome Therapeutics, Roswell Park Comprehensive Cancer Center, BreakBio, Carisma Therapeutics, CureVac, Genotwin, BioNTech, Gilead Therapeutics, Tempest Therapeutics, and the Cancer Research Institute. A.S. is a consultant for Gritstone, Flow Pharma, CellCarta, OxfordImmunotech, Immunoscape, and Avalia. La Jolla Institute for Immunology has filed for patent protection for various aspects of T cell epitope and vaccine design work. D.B.K. has previously advised Neon Therapeutics and has received consulting fees from Neon Therapeutics. D.B.K. owns equity in AduroBiotech, Agenus Inc., Armata Pharmaceuticals, Breakbio Corp., Biomarin Pharmaceutical Inc., Bristol Myers Squibb Com., Celldex Therapeutics Inc., Editas Medicine Inc., Exelixis Inc., Gilead Sciences Inc., IMV Inc., Lexicon Pharmaceuticals Inc., Moderna Inc., and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals. D.B.K. receives SARS-CoV-2 research support from BeiGene for a project unrelated to this publication. N.H. is a founder of Neon Therapeutics, Inc. (now BioNTech US), was a member of its scientific advisory board, and holds shares. N.H. is also an advisor for IFM Therapeutics. S.A.C. is a member of the scientific advisory boards of Kymera, PTM BioLabs, and Seer and a scientific advisor to Pfizer and Biogen. J.G.A. is a past employee and shareholder of Neon Therapeutics, Inc. (now BioNTech US). P.C.S. is a co-founder and shareholder of Sherlock Biosciences and a non-executive board member and shareholder of Danaher Corporation.
Figures




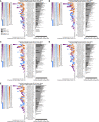
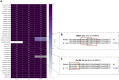
References
-
- Altman J.D., Davis M.M. MHC-Peptide Tetramers to Visualize Antigen-Specific T Cells. Curr. Protoc. Immunol. 2016;115:17.3.1–17.3.44. - PubMed
-
- Altmann D.M., Boyton R.J. SARS-CoV-2 T cell immunity: Specificity, function, durability, and role in protection. Sci. Immunol. 2020;5:eabd6160. - PubMed
-
- Bassani-Sternberg M., Gfeller D. Unsupervised HLA Peptidome Deconvolution Improves Ligand Prediction Accuracy and Predicts Cooperative Effects in Peptide-HLA Interactions. J. Immunol. 2016;197:2492–2499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

