Stepping forward in antibody-drug conjugate development
- PMID: 34171334
- PMCID: PMC8702582
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107917
Stepping forward in antibody-drug conjugate development
Abstract
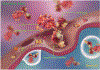
Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) are cancer therapeutic agents comprised of an antibody, a linker and a small-molecule payload. ADCs use the specificity of the antibody to target the toxic payload to tumor cells. After intravenous administration, ADCs enter circulation, distribute to tumor tissues and bind to the tumor surface antigen. The antigen then undergoes endocytosis to internalize the ADC into tumor cells, where it is transported to lysosomes to release the payload. The released toxic payloads can induce apoptosis through DNA damage or microtubule inhibition and can kill surrounding cancer cells through the bystander effect. The first ADC drug was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 2000, but the following decade saw no new approved ADC drugs. From 2011 to 2018, four ADC drugs were approved, while in 2019 and 2020 five more ADCs entered the market. This demonstrates an increasing trend for the clinical development of ADCs. This review summarizes the recent clinical research, with a specific focus on how the in vivo processing of ADCs influences their design. We aim to provide comprehensive information about current ADCs to facilitate future development.
Keywords: Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs); Cancer therapy; Clinical research; Metabolism.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Aalberse RC, Stapel SO, Schuurman J, & Rispens T (2010). Immunoglobulin G4: an odd antibody. Clinical & Experimental Allergy, 39, 469–477. - PubMed
-
- Adair JR, Howard PW, Hartley JA, Williams DG, & Chester KA (2012). Antibody-drug conjugates - a perfect synergy. Expert Opinion On Biological Therapy, 12, 1191–1206. - PubMed
-
- Ahmed F, Steele JC, Herbert JM, Steven NM, & Bicknell R (2008). Tumor stroma as a target in cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets, 8, 447–453. - PubMed
-
- Ailawadhi S, Kelly KR, Vescio RA, Jagannath S, Wolf J, Gharibo M, … Chanan-Khan A (2019). A phase I study to assess the safety and pharmacokinetics of single-agent Lorvotuzumab Mertansine (IMGN901) in patients with relapsed and/or refractory CD-56-positive multiple myeloma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk, 19, 29–34. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

