Randomised, controlled trial of erenumab for the prevention of episodic migraine in patients from Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America: The EMPOwER study
- PMID: 34171973
- PMCID: PMC8592099
- DOI: 10.1177/03331024211024160
Randomised, controlled trial of erenumab for the prevention of episodic migraine in patients from Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America: The EMPOwER study
Abstract
Objective: EMPOwER, a double-blind, randomised, phase 3 study, evaluated the efficacy and safety of erenumab in adults with episodic migraine from Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America.
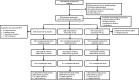
Methods: Randomised patients (N = 900) received monthly subcutaneous injections of placebo, erenumab 70 mg, or 140 mg (3:3:2) for 3 months. Primary endpoint was change from baseline in monthly migraine days at Month 3. Other endpoints included achievement of ≥50%, ≥75%, and 100% reduction in monthly migraine days, change in monthly acute migraine-specific medication treatment days, patient-reported outcomes, and safety assessment.
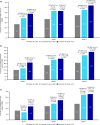
Results: At baseline, mean (standard deviation) age was 37.5 (9.9) years, 81.9% were women, and monthly migraine days was 8.2 (2.8). At Month 3, change from baseline in monthly migraine days (primary endpoint) was -3.1, -4.2, and -4.8 days for placebo, erenumab 70 mg, and erenumab 140 mg, respectively, with a statistically significant difference for erenumab versus placebo (P = 0.002 [70 mg], P < 0.001 [140 mg]). Both erenumab doses were also significantly superior to placebo on all secondary endpoints, including the proportion of patients achieving ≥50% reduction from baseline in monthly migraine days, change from baseline in monthly acute migraine-specific medication treatment days and change from baseline in the Headache Impact Test-6™ scores. The safety profile of erenumab was comparable with placebo; no new safety signals were observed.
Conclusions: This study of erenumab in patients with episodic migraine from Asia, the Middle East, and Latin America met all primary and secondary endpoints. A consistent numerical benefit was observed with erenumab 140 mg versus erenumab 70 mg across all efficacy endpoints. These findings extend evidence of erenumab's efficacy and safety to patients under-represented in previous trials.ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03333109.
Keywords: Asia; Latin America; calcitonin gene-related peptide; episodic migraine; erenumab; randomised controlled trial.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Woldeamanuel YW, Cowan RP. Migraine affects 1 in 10 people worldwide featuring recent rise: a systematic review and meta-analysis of community-based studies involving 6 million participants. J Neur Sc 2017; 372: 307–315. - PubMed
-
- GBD 2016 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators . Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990–2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017; 390: 1211–1259. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buse DC, Scher AI, Dodick DW, et al. Impact of migraine on the family: perspectives of people with migraine and their spouse/domestic partner in the CaMEO study. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2016; 91: 596–611. - PubMed
-
- Blumenfeld AM, Varon SF, Wilcox TK, et al. Disability, HRQoL and resource use among chronic and episodic migraineurs: results from the International Burden of Migraine Study (IBMS). Cephalalgia 2011; 31: 301–315. - PubMed
-
- Bonafede M, Sapra S, Shah N, et al. Direct and indirect healthcare resource utilization and costs among migraine patients in the United States. Headache 2018; 58: 700–714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

