Characterization of the antibacterial activity from ethanolic extracts of the botanical, Larrea tridentata
- PMID: 34172064
- PMCID: PMC8235861
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-021-03344-9
Characterization of the antibacterial activity from ethanolic extracts of the botanical, Larrea tridentata
Abstract
Background: β-lactam antibiotics are a class of broad-spectrum antibiotics consisting of all antibiotic agents that contain a β-lactam ring in their molecular structures. β-lactam antibiotics are only known to be isolated from fungi (e.g. Acremonium chrysogenum, Penicillium chrysogenum and Aspergillus nidulans) and bacteria (e.g. Streptomyces clavuligerus). We have shown that botanical extracts prepared from Larrea tridentata have strong antimicrobial activity against several bacteria, including members of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus genera.
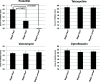
Methods: Through resistance studies, inhibitor assays, and ELISA testing, we demonstrated L. tridentata extracts may contain a β-lactam type antibiotic activity.
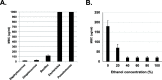
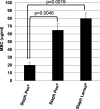
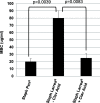
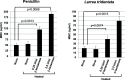
Results: Based on the estimated β-lactam concentration within the extract, the antimicrobial activity of the L. tridentata extract was approximately 2000-8000-fold greater against Staphylococcus as compared to other β-lactams, penicillin or ampicillin. In the L. tridentata extract, this increased activity was found to be associated with the likely presence of a cofactor leading to increased potentiation of the β-lactam activity. This potentiation activity was also observed to enhance the activity of exogenously added natural penicillin antibiotics.
Conclusions: Although constituents were not isolated in this study, the results obtained strongly support the presence of β-lactam type antibiotic activity and antibiotic potentiation activity present in ethanolic extracts prepared from L. tridentata.
Keywords: Antibiotic; Antimicrobials; Bacteria; Larrea tridentata; Staphylococcus aureus; Tincture; β-Lactam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication and there has been no significant financial support for this works that could have influenced its outcome. The authors are not members of the editorial board for this journal.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Larrea tridentata Extracts and Their Antimicrobial Effects on Strains of Clinical Interest.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 25;26(3):1032. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031032. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940800 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial and antimycobacterial lignans and flavonoids from Larrea tridentata.Phytother Res. 2012 Dec;26(12):1957-60. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4660. Epub 2012 Mar 15. Phytother Res. 2012. PMID: 22422605
-
The antibacterial activity of extracts of nine plant species with good activity against Escherichia coli against five other bacteria and cytotoxicity of extracts.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Feb 28;17(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1645-z. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28241818 Free PMC article.
-
Production of beta-lactam antibiotics and its regulation.Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 1991 Oct;15(4):251-65. Proc Natl Sci Counc Repub China B. 1991. PMID: 1815263 Review.
-
Larrea tridentata and its Biological Activities.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(26):2352-2364. doi: 10.2174/1568026621666210727170908. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 34315376 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbicidal Activity of Extract Larrea tridentata (Sessé and Moc. ex DC.) Coville on Pseudomonas syringae Van Hall and Botrytis cinerea Pers.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 30;13(5):1055. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13051055. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40431227 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Larrea tridentata Extracts and Their Antimicrobial Effects on Strains of Clinical Interest.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 25;26(3):1032. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031032. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940800 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro characterization of potential botanicals to reduce infection and improve the rate of wound healing in humans and canines.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Feb 14;25(1):55. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04777-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 39953529 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Compounds and Pharmacological Properties of Larrea tridentata.Molecules. 2022 Aug 24;27(17):5393. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175393. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
nor 3'-Demethoxyisoguaiacin from Larrea tridentata Is a Potential Alternative against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria Associated with Bovine Mastitis.Molecules. 2022 Jun 5;27(11):3620. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113620. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684556 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

