Adipokine Apelin/APJ Pathway Promotes Peritoneal Dissemination of Ovarian Cancer Cells by Regulating Lipid Metabolism
- PMID: 34172534
- PMCID: PMC11486291
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0991
Adipokine Apelin/APJ Pathway Promotes Peritoneal Dissemination of Ovarian Cancer Cells by Regulating Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
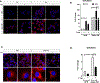
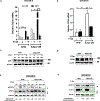
Adipose tissue, which can provide adipokines and nutrients to tumors, plays a key role in promoting ovarian cancer metastatic lesions in peritoneal cavity. The adipokine apelin promotes ovarian cancer metastasis and progression through its receptor APJ, which regulates cell proliferation, energy metabolism, and angiogenesis. The objective of this study was to investigate the functional role and mechanisms of the apelin-APJ pathway in ovarian cancer metastasis, especially in context of tumor cell-adipocyte interactions. When co-cultured in the conditioned media (AdipoCM) derived from 3T3-L1 adipocytes, which express and secrete high apelin, human ovarian cancer cells with high APJ expression showed significant increases in migration and invasion in vitro. We also found that cells expressing high levels of APJ had increased cell adhesion to omentum ex vivo, and preferentially "home-in" on the omentum in vivo. These apelin-induced pro-metastatic effects were reversed by APJ antagonist F13A in a dose-dependent manner. Apelin-APJ activation increased lipid droplet accumulation in ovarian cancer cells, which was further intensified in the presence of AdipoCM and reversed by F13A or APJ knockdown. Mechanistically, this increased lipid uptake was mediated by CD36 upregulation via APJ-STAT3 activation, and the lipids were utilized in promoting fatty acid oxidation via activation of AMPK-CPT1a axis. Together, our studies demonstrate that adipocyte-derived apelin activates APJ-expressing tumor cells in a paracrine manner, promoting lipid uptake and utilization and providing energy for ovarian cancer cell survival at the metastatic sites. Hence, the apelin-APJ pathway presents a novel therapeutic target to curb ovarian cancer metastasis. IMPLICATIONS: Targeting the APJ pathway in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma is a novel strategy to inhibit peritoneal metastasis.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS:
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Multifunctional APJ Pathway Promotes Ovarian Cancer Progression and Metastasis.Mol Cancer Res. 2019 Jun;17(6):1378-1390. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-18-0989. Epub 2019 Mar 11. Mol Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30858172 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of apelin and apelin receptor (APJ) in porcine ovarian follicles and in vitro effect of apelin on steroidogenesis and proliferation through APJ activation and different signaling pathways.Theriogenology. 2017 Jul 1;96:126-135. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2017.04.014. Epub 2017 Apr 7. Theriogenology. 2017. PMID: 28532828
-
Single-cell and spatial transcriptomics reveal apelin/APJ pathway's role in microvessel formation and tumour progression in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Oct;28(20):e70152. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70152. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39434201 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Apelin/APJ axis in cancer development and progression.Adv Med Sci. 2020 Mar;65(1):202-213. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2020.02.002. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Adv Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32087570 Review.
-
Apelin/APJ: Another Player in the Cancer Biology Network.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 25;26(7):2986. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072986. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243599 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-angiogenic therapy in ovarian cancer: Current understandings and prospects of precision medicine.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 7;14:1147717. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1147717. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36959862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
EIF4A3 Acts on the PI3K-AKT-ERK1/2-P70S6K Pathway through FLOT1 to Influence the Development of Lung Adenocarcinoma.Mol Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 5;21(7):713-725. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-22-0984. Mol Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37011005 Free PMC article.
-
Adipo-oncology: adipocyte-derived factors govern engraftment, survival, and progression of metastatic cancers.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jan 18;22(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01474-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38238841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SLCO4A1 expression is associated with activated inflammatory pathways in high-grade serous ovarian cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 29;13:946348. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.946348. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36105223 Free PMC article.
-
Clinacanthus nutans (Burm.f.) Lindau facilitates cuproptosis and ameliorates colon cancer progression by inhibiting PDE3B-mediated Apelin pathway.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 11;16(1):1521. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-02037-w. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40788438 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

