Simultaneous multi-nuclide imaging via double-photon coincidence method with parallel hole collimators
- PMID: 34172772
- PMCID: PMC8233320
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-92583-4
Simultaneous multi-nuclide imaging via double-photon coincidence method with parallel hole collimators
Abstract
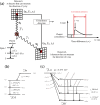
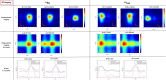
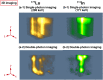
Multi-tracer imaging can provide useful information in the definitive diagnosis and research of medical, biological, and pharmaceutical sciences. Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) is one of the nuclear medicine imaging modalities widely used for diagnosis or medical research and has a multi-tracer imaging capability. One of the drawbacks of multi-tracer imaging is crosstalk from other gamma rays, which affects the reconstructed image. Scattering correction methods, such as the dual- and triple-energy window methods, are used for conventional SPECT imaging to reduce the background caused by the crosstalk. This study proposes another crosstalk reduction method. Some nuclides emit two or more gamma rays through intermediate levels. Thus, detecting these gamma rays with the coincidence method allows us to distinguish a true gamma ray signal and a background signal. The nuclide position can be estimated at the intersection of two gamma rays using collimators. We demonstrate herein simultaneous 111In and 177Lu imaging via the double-photon coincidence method using GAGG detectors and parallel hole collimators. The double-photon coincidence method greatly reduces the background caused by other gamma rays and offers higher-quality images than does conventional imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Feasibility of dual-isotope coincidence/single-photon imaging of the myocardium.J Nucl Med. 2001 Jun;42(6):944-50. J Nucl Med. 2001. PMID: 11390561
-
Positron emission tomography with additional γ-ray detectors for multiple-tracer imaging.Med Phys. 2017 Jun;44(6):2257-2266. doi: 10.1002/mp.12149. Epub 2017 May 4. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28168704
-
Simultaneous fluoroscopic and nuclear imaging: impact of collimator choice on nuclear image quality.Med Phys. 2017 Jan;44(1):249-261. doi: 10.1002/mp.12010. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28044322
-
Compton imaging for medical applications.Radiol Phys Technol. 2022 Sep;15(3):187-205. doi: 10.1007/s12194-022-00666-2. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Radiol Phys Technol. 2022. PMID: 35867197 Review.
-
SPECT instrumentation: performance, lesion detection, and recent innovations.Semin Nucl Med. 1987 Jul;17(3):184-99. doi: 10.1016/s0001-2998(87)80033-8. Semin Nucl Med. 1987. PMID: 3303339 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous in vivo imaging with PET and SPECT tracers using a Compton-PET hybrid camera.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 9;11(1):17933. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97302-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34504184 Free PMC article.
-
Current and potential roles of immuno-PET/-SPECT in CAR T-cell therapy.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jun 27;10:1199146. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1199146. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37441689 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Forrer F, Waldherr C, Maecke HR, Mueller-Brand J. Targeted radionuclide therapy with 90Y-DOTATOC in patients with neuroendocrine tumors. Anticancer Res. 2006;26:703–707. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

