Serum IgG4 levels at diagnosis can predict unfavorable outcomes of untreated patients with IgG4-related disease
- PMID: 34172819
- PMCID: PMC8233326
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-92814-8
Serum IgG4 levels at diagnosis can predict unfavorable outcomes of untreated patients with IgG4-related disease
Abstract
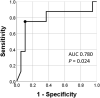
The outcomes of patients with immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4)-related disease (IgG4-RD) who are not treated are unclear. This study aimed to clarify these outcomes and identify the factors related to them. We retrospectively evaluated various clinical features including laboratory data and involved organs at diagnosis in 107 patients with IgG4-RD, who were followed up for more than 6 months, at a single center in Japan. We compared the clinical features of the 27 untreated patients with those of the 80 patients treated with glucocorticoid. The patient outcomes were investigated, and logistic regression analysis was performed to identify factors related to them. The patients comprised 73 men and 34 women (median age 67 years). The untreated patients had significantly lower IgG4-RD responder index (9 vs. 12) and fewer affected organs (1 vs. 3) than did those treated with glucocorticoid. Of these 27 patients, 8 experienced deterioration of IgG4-RD after the diagnosis. In the age- and sex-adjusted logistic regression analysis, serum IgG4 elevation (per 100 mg/dL, odds ratio 1.194, 95% confidence interval 1.017-1.402) was the only significant factor related to disease deterioration in untreated patients with IgG4-RD, whereas not serum IgG4 levels (per 100 mg/dL, odds ratio 0.995, 95% confidence interval 0.921-1.075) but history of allergy (OR 3.134, 95% confidence interval 1.094-8.977, P = 0.033) related to deterioration in patients who underwent treatment. Serum IgG4 levels may be a useful predictor of unfavorable outcomes in untreated patients with IgG4-RD, who tend to have fewer affected organs and lower IgG4-RD responder index.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differences and similarities between IgG4-related disease with and without dacryoadenitis and sialoadenitis: clinical manifestations and treatment efficacy.Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 Feb 1;21(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13075-019-1828-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30709411 Free PMC article.
-
Serum immunoglobulin free light chains and their association with clinical phenotypes, serology and activity in patients with IgG4-related disease.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 19;11(1):1832. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81321-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33469111 Free PMC article.
-
Increase of circulating memory B cells after glucocorticoid-induced remission identifies patients at risk of IgG4-related disease relapse.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Oct 3;20(1):222. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1718-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30285841 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoglobulin G4 (IgG4) Positive Associated Liver Disease.Clin Lab. 2024 May 1;70(5). doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2023.231218. Clin Lab. 2024. PMID: 38747922 Review.
-
Combination therapy of leflunomide and glucocorticoids for the maintenance of remission in patients with IgG4-related disease: a retrospective study and literature review.Intern Med J. 2017 Jun;47(6):680-689. doi: 10.1111/imj.13430. Intern Med J. 2017. PMID: 28321964 Review.
Cited by
-
Pathological count of IgG4-positive plasmacytes suggests extraophthalmic involvement and relapse in patients with IgG4-related ophthalmic disease: a retrospective study.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Apr 1;24(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02757-2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35365184 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Performance of Immunonephelometric Assay and Chemiluminescent Immunoassay for Detection of IgG Subclasses in Chinese.J Clin Lab Anal. 2024 Apr;38(8):e25033. doi: 10.1002/jcla.25033. Epub 2024 Apr 2. J Clin Lab Anal. 2024. PMID: 38563457 Free PMC article.
-
A case of IgG4-related ophthalmic disease after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination: case report and literature review.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 22;15:1303589. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1303589. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38455056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Laboratory characteristics of IgG4-related disease: A retrospective study from a single tertiary medical center.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Sep 9;101(36):e30387. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000030387. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36086780 Free PMC article.
-
Immune Profile Differences between IgG4-Related Diseases and Primary Sjögren's Syndrome.J Inflamm Res. 2025 Jan 21;18:911-923. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S471266. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39871956 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

