p38-MAPK-mediated translation regulation during early blastocyst development is required for primitive endoderm differentiation in mice
- PMID: 34172827
- PMCID: PMC8233355
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-021-02290-z
p38-MAPK-mediated translation regulation during early blastocyst development is required for primitive endoderm differentiation in mice
Abstract
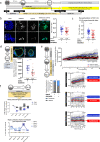
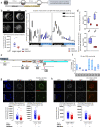
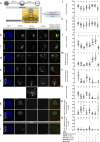
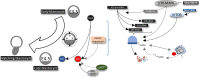
Successful specification of the two mouse blastocyst inner cell mass (ICM) lineages (the primitive endoderm (PrE) and epiblast) is a prerequisite for continued development and requires active fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF4) signaling. Previously, we identified a role for p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (p38-MAPKs) during PrE differentiation, but the underlying mechanisms have remained unresolved. Here, we report an early blastocyst window of p38-MAPK activity that is required to regulate ribosome-related gene expression, rRNA precursor processing, polysome formation and protein translation. We show that p38-MAPK inhibition-induced PrE phenotypes can be partially rescued by activating the translational regulator mTOR. However, similar PrE phenotypes associated with extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) pathway inhibition targeting active FGF4 signaling are not affected by mTOR activation. These data indicate a specific role for p38-MAPKs in providing a permissive translational environment during mouse blastocyst PrE differentiation that is distinct from classically reported FGF4-based mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
p38 (Mapk14/11) occupies a regulatory node governing entry into primitive endoderm differentiation during preimplantation mouse embryo development.Open Biol. 2016 Sep;6(9):160190. doi: 10.1098/rsob.160190. Open Biol. 2016. PMID: 27605380 Free PMC article.
-
DDX21 is a p38-MAPK-sensitive nucleolar protein necessary for mouse preimplantation embryo development and cell-fate specification.Open Biol. 2021 Jul;11(7):210092. doi: 10.1098/rsob.210092. Epub 2021 Jul 14. Open Biol. 2021. PMID: 34255976 Free PMC article.
-
PI3K/AKT signaling controls ICM maturation and proper epiblast and primitive endoderm specification in mice.Dev Cell. 2025 Jan 20;60(2):204-219.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2024.10.001. Epub 2024 Oct 25. Dev Cell. 2025. PMID: 39461340
-
Primitive endoderm differentiation: from specification to epithelium formation.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014 Dec 5;369(1657):20130537. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0537. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25349446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell lineage allocation within the inner cell mass of the mouse blastocyst.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2012;55:185-202. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-30406-4_10. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2012. PMID: 22918807 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling pathway regulators in preimplantation embryos.J Mol Histol. 2024 Dec 27;56(1):57. doi: 10.1007/s10735-024-10338-7. J Mol Histol. 2024. PMID: 39729177 Review.
-
Gpr37 modulates the severity of inflammation-induced GI dysmotility by regulating enteric reactive gliosis.iScience. 2025 Jun 16;28(7):112885. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112885. eCollection 2025 Jul 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40678517 Free PMC article.
-
Irisin Enhances Mitochondrial Function in Osteoclast Progenitors during Differentiation.Biomedicines. 2023 Dec 14;11(12):3311. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11123311. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 38137532 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of mitochondrial unfolded protein response results in telomere shortening in mouse oocytes and somatic cells.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Feb 12;16(3):2047-2060. doi: 10.18632/aging.205543. Epub 2024 Feb 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38349865 Free PMC article.
-
Human REXO4 is Required for Cell Cycle Progression.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 9:2025.01.08.631954. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.08.631954. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39829749 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

