Plasma therapy cured a COVID-19 patient with long duration of viral shedding for 49 days: The clinical features, laboratory tests, plasma therapy, and implications for public health management
- PMID: 34172984
- PMCID: PMC7262084
- DOI: 10.1002/mco2.2
Plasma therapy cured a COVID-19 patient with long duration of viral shedding for 49 days: The clinical features, laboratory tests, plasma therapy, and implications for public health management
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
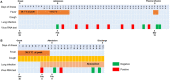
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources