SEC61G identified as a prognostic biomarker of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 34173014
- PMCID: PMC8930941
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-021-06955-7
SEC61G identified as a prognostic biomarker of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Purpose: It is of obvious interest to identify clinical prognosis-related oncogenes in HNSCC (head and neck squamous cell carcinoma).
Methods: Based on the available datasets within the TCGA (The Cancer Genome Atlas) and the GEO (Gene Expression Omnibus) databases, the potential mechanism of action of the SEC61G (SEC61 translocon subunit gamma) gene in HNSCC tumorigenesis was explored by several bioinformatics approaches.
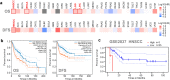
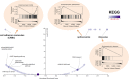
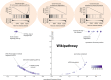
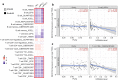
Results: There was a higher expression level of SEC61G in primary HNSCC tumor tissues than in normal tissues. Moreover, highly expressed SEC61G was statistically associated with the poor survival prognosis of HNSCC patients. When HPV (human papilloma virus) was considered, we also observed a relatively lower proportion of "arm-level gain" and "high amplification" types of CNA (copy-number alteration) in the HNSCC-HPV (+) group than in the HNSCC-HPV (-) group. Additionally, we identified SEC61G CAN-correlated genes, such as CCT6A (chaperonin-containing TCP1 subunit 6A) and HUS1 (HUS1 checkpoint clamp component), and found a correlation between SEC61G copy-number segments and prognosis related to overall and progression-free survival intervals of HNSCC patients. Moreover, the molecular regulation mechanisms of the spliceosome, ribosome, proteasome degradation, cell adhesion, and immune infiltration of B and CD8+ T cells may contribute to the involvement of SEC61G in the pathogenesis of HNSCC.
Conclusions: The SEC61G gene was identified for the first time as a prognostic biomarker of HNSCC. The detailed underlying mechanism merits further research.
Keywords: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; Prognosis; SEC61G; TCGA.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SEC61G overexpression and DNA amplification correlates with prognosis and immune cell infiltration in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2021 Nov;10(21):7847-7862. doi: 10.1002/cam4.4301. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Cancer Med. 2021. PMID: 34590792 Free PMC article.
-
High SEC61G expression predicts poor prognosis in patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas.J Cancer. 2021 May 5;12(13):3887-3899. doi: 10.7150/jca.51467. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34093796 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor Mutation Burden, Immune Cell Infiltration, and Construction of Immune-Related Genes Prognostic Model in Head and Neck Cancer.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 1;18(1):226-238. doi: 10.7150/ijms.51064. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33390791 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive review regarding the association of E2Fs with the prognosis and immune infiltrates in human head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Asian J Surg. 2024 May;47(5):2106-2121. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2024.01.130. Epub 2024 Feb 5. Asian J Surg. 2024. PMID: 38320907 Review.
-
Molecular and biological factors in the prognosis of head and neck squamous cell cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2023 Sep;50(9):7839-7849. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08611-1. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Mol Biol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37493876 Review.
Cited by
-
SEC61 translocon gamma subunit is correlated with glycolytic activity, epithelial mesenchymal transition and the immune suppressive phenotype of lung adenocarcinoma.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 Jul 8;56(12):1748-1760. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024109. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38978503 Free PMC article.
-
SEC61G participates in endoplasmic reticulum stress by interacting with CREB3 to promote the malignant progression of lung adenocarcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2022 May 30;24(1):233. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13316. eCollection 2022 Jul. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35720482 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of myosin genes in HNSCC and identify MYL1 as a specific poor prognostic biomarker, promotes tumor metastasis and correlates with tumor immune infiltration in HNSCC.BMC Cancer. 2023 Sep 7;23(1):840. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11349-5. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37679666 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of SEC61G as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Biomedicines. 2023 Oct 6;11(10):2718. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11102718. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37893092 Free PMC article.
-
SEC61 translocon subunit gamma enhances low-dose cisplatin-induced cancer-stem cell properties of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma via enhancing Ca2+-mediated autophagy.J Dent Sci. 2023 Oct;18(4):1685-1692. doi: 10.1016/j.jds.2023.01.024. Epub 2023 Feb 4. J Dent Sci. 2023. PMID: 37799908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Staneva R, Rukova B, Hadjidekova S, Nesheva D, Antonova O, Dimitrov P, Simeonov V, Stamenov G, Cukuranovic R, Cukuranovic J, Stefanovic V, Polenakovic M, Dimova I, Hlushchuk R, Djonov V, Galabov A, Toncheva D. Whole genome methylation array analysis reveals new aspects in Balkan endemic nephropathy etiology. BMC Nephrol. 2013;14:225. doi: 10.1186/1471-2369-14-225. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

