Homeostatic alterations related to total antioxidant capacity, elemental concentrations and isotopic compositions in aqueous humor of glaucoma patients
- PMID: 34173037
- PMCID: PMC8748375
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-021-03467-5
Homeostatic alterations related to total antioxidant capacity, elemental concentrations and isotopic compositions in aqueous humor of glaucoma patients
Abstract
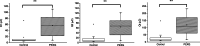
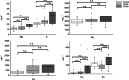
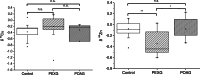
Glaucoma is a multifactorial eye disease, characterized by progressive optic neurodegeneration. Elevation of the intraocular pressure is the main risk factor for glaucoma and is a consequence of an imbalance in the aqueous humor hydrodynamics, the physiology of which is influenced by the homeostatic equilibrium of essential elements, oxidative stress, and antioxidants. The aim of this work was to study local alterations in glaucomatous patients from two different, but connected, points of view: (i) the total antioxidant capacity (as an indicator of oxidative damage) and (ii) the concentration of mineral elements and their isotopic composition. Such objective was pursued using aqueous humor from patients diagnosed with pseudoexfoliation glaucoma (PEXG, n = 17) and primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG, n = 5) and age-matched control subjects (n = 16). The total antioxidant capacity (TAC) was examined in both aqueous humor and 60 serum samples (n = 20 controls, n = 20 for PEXG, and n = 20 for POAG), both showing higher TAC for the glaucoma population. The concentrations of the essential mineral elements (Cu, Fe, Mg, Na, P, and Zn) and the isotopic compositions of Cu and Zn were determined in aqueous humor using single-collector and multi-collector inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry, respectively. Significant differences were established for Mg and P levels when comparing the results for glaucomatous patients with those for the control population (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05 for Mg and P respectively, ANOVA and Kruskal-Wallis). The Zn isotopic composition was significantly shifted from that for the control population for PEXG patients. A significant difference in the isotopic composition of Zn was also established between the PEXG and POAG glaucoma cohorts.
Keywords: Aqueous humor; Elemental concentration; Inductively coupled plasma–mass spectrometry; Isotopic composition; Pseudoexfoliation glaucoma.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of serum and aqueous humor klotho levels in pseudoexfoliation syndrome, pseudoexfoliation and primary open-angle glaucoma.Int Ophthalmol. 2021 Jul;41(7):2369-2375. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-01790-5. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Int Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33738657
-
Levels of aqueous humor trace elements in patients with open-angle glaucoma.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2018 Jan;45:150-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2017.10.003. Epub 2017 Oct 12. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29173472
-
Aqueous humor selenium level and open-angle glaucoma.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2018 Dec;50:67-72. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2018.06.010. Epub 2018 Jun 19. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30262318
-
Specific Biomarkers in the Aqueous Humour of Glaucoma Patients.Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2022 Feb;239(2):169-176. doi: 10.1055/a-1690-7468. Epub 2022 Feb 24. Klin Monbl Augenheilkd. 2022. PMID: 35211939 Review. English, German.
-
Bioinorganic chemistry of open-angle glaucoma: A review.J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020 Dec;62:126652. doi: 10.1016/j.jtemb.2020.126652. Epub 2020 Sep 22. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32987352 Review.
Cited by
-
Levels of Zinc, Iron, and Copper in the Aqueous Humor of Patients with Primary Glaucoma.Biomolecules. 2025 Jul 4;15(7):962. doi: 10.3390/biom15070962. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40723834 Free PMC article.
-
Deciphering Antioxidant Responses in Tomato Autografts.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Feb 18;14(2):234. doi: 10.3390/antiox14020234. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40002418 Free PMC article.
-
More light components and less light damage on rats' eyes: evidence for the photobiomodulation and spectral opponency.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2023 Apr;22(4):809-824. doi: 10.1007/s43630-022-00354-5. Epub 2022 Dec 17. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36527588
-
Metallothioneins, a Part of the Retinal Endogenous Protective System in Various Ocular Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jun 10;12(6):1251. doi: 10.3390/antiox12061251. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Viscum album Extracts: Unveiling Bioactive Compounds, Antibacterial Potential, and Antioxidant Activities.Plants (Basel). 2023 May 27;12(11):2130. doi: 10.3390/plants12112130. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37299109 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jonas JB, Aung T, Ritch R, Panda-Jonas S. Glaucoma. Lancet. 2017;390:2813–2193. - PubMed
-
- Kerrigan-Baumrind LA, Quigley HA, Pease ME, Kerrigan DF, Mitchell RS. Number of ganglion cells in glaucoma eyes compared with threshold visual field tests in the same persons. Investig Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2000;41:741–748. - PubMed
-
- Gabelt BT, Kaufman PL. Changes in aqueous humor dynamics with age and glaucoma. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2005;24:612–637. - PubMed
-
- Ritch R, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U. Exfoliation syndrome. Surv Ophthalmol. 2001;45:265–315. - PubMed
-
- Rand Allingham R, Bruce Shields M, Damji KF, Shafranov G. Shields textbook of glaucoma. 5. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2005.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ZW15-02 - G0H6216N/Fonds Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek
- project CTQ2016-79015-R/Agencia Estatal de Investigación (Spain) and FEDER
- "Plan de Apoyo y Promoción de la investigació/M. A. thanks University of Oviedo her predoctoral Grant
- project IDE/2019/000289/Instituto de Desarrollo Económico del Principado de Asturias of Gobierno del Principado de Asturias
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

