Next-generation sequencing of tissue and circulating tumor DNA: Resistance mechanisms to EGFR targeted therapy in a cohort of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 34173341
- PMCID: PMC8290257
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.3948
Next-generation sequencing of tissue and circulating tumor DNA: Resistance mechanisms to EGFR targeted therapy in a cohort of patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
Background: Epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) has been considered as an effective treatment in epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant (EGFR-mutant) advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, most patients develop acquired resistance eventually. Here, we compared and analyzed the genetic alterations between tissue assay and circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) and further explored the resistance mechanisms after EGFR-TKI treatment.
Methods and materials: Amplification refractory mutation system-polymerase chain reaction (ARMS-PCR), Cobas® ARMS-PCR and next-generation sequencing (NGS) were performed on tissue samples after pathological diagnosis. Digital droplet PCR (ddPCR) and NGS were performed on plasma samples. The association between genetic alterations and clinical outcomes was analyzed retrospectively.
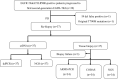
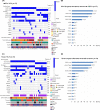
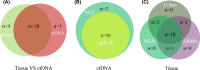
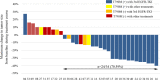
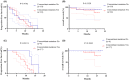
Results: Thirty-seven patients were included. The success rate of re-biopsy was 91.89% (34/37). The total detection rate of EGFR T790M was 62.16% (23/37) and the consistency between tissue and ctDNA was 78.26% (18/23). Thirty-four patients were analyzed retrospectively. For tissue re-biopsy, 24 patients harbored concomitant mutations. Moreover, tissue re-biopsy at resistance showed 21 patients (21/34, 61.76%) had the concomitant somatic mutation. The three most frequent concomitant mutations were TP53 (18/34, 52.94%), MET (4/34, 11.76%), and PIK3CA (4/34, 11.76%). Meanwhile, 21 patients (21/34, 61.76%) with EGFR T790M mutation. Progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were better in patients with T790M mutation (p = 0.010 and p = 0.017) or third-generation EGFR-TKI treatment (p < 0.0001 and p = 0.073). Interestingly, concomitant genetic alterations were significantly associated with a worse prognosis for patients with EGFR T790M mutation receiving third-generation EGFR-TKIs (p = 0.037).
Conclusions: Multi-platforms are feasible and highly consistent for re-biopsy after EGFR-TKI resistance. Concomitant genetic alterations may be associated with a poor prognosis for patients with EGFR T790M mutation after third-generation EGFR-TKIs.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT03309462.
Keywords: epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI); genetic alterations; non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC); re-biopsy.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394‐424. - PubMed
-
- Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, et al. Changing epidemiology of small‐cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol. 2006;24:4539‐4544. - PubMed
-
- Lindeman NI, Cagle PT, Beasley MB, et al. Molecular testing guideline for selection of lung cancer patients for EGFR and ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors: guideline from the College of American Pathologists, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, and Association for Molecular Pathology. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8:823‐859. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

