Impact of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) and intestine-specific homeobox (ISX) expression on the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma' for better clarity
- PMID: 34173348
- PMCID: PMC8366091
- DOI: 10.1002/cam4.4094
Impact of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) and intestine-specific homeobox (ISX) expression on the prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma' for better clarity
Abstract
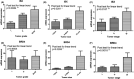
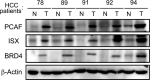
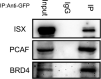
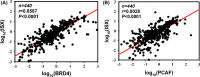
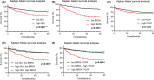
Epigenetic regulation is important for cancer tumor metastasis and progression, including lung and liver cancer. However, the mechanism of epigenetic regulation in liver cancer leaves much to be discussed. According to a previous study, p300/CBP-associated factor (PCAF) mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and promotes cancer metastasis by recruiting intestine-specific homeobox (ISX) and bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) in lung cancer. To figure out whether the three genes are also expressed in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) or not, and their correlation with patients' outcome, BRD4, PCAF, and ISX messenger RNA (mRNA) expression levels in 377 patients with HCC were investigated using quantitative polymerase chain reaction and confocal fluorescence imaging. The correlation of the gene expression (PCAF, ISX, and BRD4) in liver cancer is also being investigated. Here, we show that the mRNA expression of PCAF, BRD4, and ISX in 377 paired specimens from patients with HCC, and the adjacent normal tissues exhibited a tumor-specific expression pattern, highly correlated with disease pathogenesis, patient survival time, progression stage, and poor prognosis. The results show that ISX and BRD4 can potentially be a target for improving the survival rate.
Keywords: BRD4; HCC; ISX.
© 2021 The Authors. Cancer Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There is none
Figures
References
-
- El‐Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132(7):2557‐2576. - PubMed
-
- Management consensus guideline for hepatocellular carcinoma: 2016 updated by the Taiwan Liver Cancer Association and the Gastroenterological Society of Taiwan. J Formos Med Assoc. 2018;117(5):381‐403. - PubMed
-
- Sangiovanni A, Prati GM, Fasani P, et al. The natural history of compensated cirrhosis due to hepatitis C virus: a 17‐year cohort study of 214 patients. Hepatology. 2006;43(6):1303‐1310. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

