Erk phosphorylation reduces the thymoquinone toxicity in human hepatocarcinoma
- PMID: 34173702
- PMCID: PMC8456969
- DOI: 10.1002/tox.23317
Erk phosphorylation reduces the thymoquinone toxicity in human hepatocarcinoma
Abstract
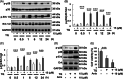
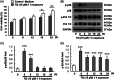
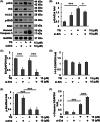
Although enormous achievements have been made in targeted molecular therapies against hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the treatments can only prolong the life of patients with extrahepatic metastases. We evaluated thymoquinone (TQ), a compound from Nigella sativa Linn., for its anti-cancer effect on SK-Hep1 cells and HCC-xenograft nude mice. TQ effectively triggered cell death and activated p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinases (Erk) pathways up to 24 h after treatment in cells. TQ-induced cell death was reversed by p38 inhibitor; however, it was enhanced by si-Erk. The caspase3 activation and TUNEL assay revealed a stronger toxic effect upon co-treatment with TQ and si-Erk. Our study suggested that phosphorylation of p38 in SK-Hep1 cells constituted the major factor leading to cell apoptosis, whereas phosphorylation of Erk led to drug resistance. Furthermore, TQ therapeutic effect was improved upon Erk inhibition in HCC-xenograft nude mice. TQ could present excellent anti-HCC potential under suitable p-Erk inhibiting conditions.
Keywords: Erk; SK-Hep1 cells; hepatocellular carcinoma; p38; thymoquinone.
© 2021 The Authors. Environmental Toxicology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet‐Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:87‐108. - PubMed
-
- Wang WY, Qin HL, Zhou L, Ma JL. Meta‐analysis of the relationship between microRNA‐499 rs3746444 polymorphism and hepatocellular carcinoma risk in Asians. J Cancer Res Ther. 2016;12:676‐680. - PubMed
-
- Hsu SC, Kuo CL, Lin JP, et al. Crude extracts of Euchresta formosana radix inhibit invasion and migration of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2007;27:2377‐2384. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

