Clinical outcome of CIDP one year after start of treatment: a prospective cohort study
- PMID: 34173873
- PMCID: PMC8782785
- DOI: 10.1007/s00415-021-10677-5
Clinical outcome of CIDP one year after start of treatment: a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: To assess clinical outcome in treatment-naive patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (CIDP).
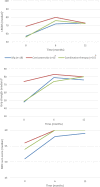
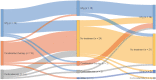
Methods: We included adult treatment-naive patients participating in the prospective International CIDP Outcome Study (ICOS) that fulfilled the European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society (EFNS/PNS) diagnostic criteria for CIDP. Patients were grouped based on initial treatment with (1) intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg), (2) corticosteroid monotherapy or (3) IVIg and corticosteroids (combination treatment). Outcome measures included the inflammatory Rasch-built overall disability scale (I-RODS), grip strength, and Medical Research Council (MRC) sum score. Treatment response, treatment status, remissions (improved and untreated), treatment changes, and residual symptoms or deficits were assessed at 1 year.
Results: Forty patients were included of whom 18 (45%) initially received IVIg, 6 (15%) corticosteroids, and 16 (40%) combination treatment. Improvement on ≥ 1 of the outcome measures was seen in 31 (78%) patients. At 1 year, 19 (48%) patients were still treated and fourteen (36%) patients were in remission. Improvement was seen most frequently in patients started on IVIg (94%) and remission in those started on combination treatment (44%). Differences between groups did not reach statistical significance. Residual symptoms or deficits ranged from 25% for neuropathic pain to 96% for any sensory deficit.
Conclusions: Improvement was seen in most patients. One year after the start of treatment, more than half of the patients were untreated and around one-third in remission. Residual symptoms and deficits were common regardless of treatment.
Keywords: CIDP; Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy; Corticosteroids; Intravenous immunoglobulin.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
SB reports no disclosures; MB reports report grants from the Dutch Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds, during the conduct of the study; IL reports no disclosures; CB reports no disclosures; GvL reports no disclosures; MA reports no disclosures; RvV reports no disclosures; LW reports to have received research grants from Amsterdam UMC Neuroscience, Grifols and the GBS|CIDP Foundation for the study of disease activity biomarkers in CIDP; HL reports grants from the Dutch Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds, during the conduct of the study; HG has received research support from Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds, travel grants and speaker fee from Takeda/ShireHG report; WvdP reports; IvS chaired a steering committee for a CSL-Behring study investigating the safety and efficacy of SCIg in CIDP and received departmental honoraria for serving on scientific advisory boards for CSL-Behring and Kedrion. He received departmental research support from The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research, and from the Dutch Prinses Beatrix Fonds. All lecturing and consulting fees for INS were donated to the Stichting Klinische Neurologie, a local foundation that supports research in the field of neurological disorders. He served on the editorial board of the Cochrane Neuromuscular Disease Group, was a member of the organizing committee of the Inflammatory Neuropathy Consortium (INC), a standing committee of the Peripheral Nerve Society and was a member of the Scientific Board of the Kreuth III meeting on the optimal use of plasma-derived medicinal products, especially coagulation factors and normal immunoglobulins organized under the auspices of the European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & HealthCare (EDQM); PvD reports grants from Takeda, during the conduct of the study; grants from Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds, grants from Sanquin Blood Supply, grants from Grifols, other from Hansa, Annexion, Argenx, CSL, and Octapharma, outside the submitted work; BJ reports grants from Dutch Prinses Beatrix Spierfond, during the conduct of the study; grants from Dutch Prinses Beatrix Spierfonds, Horizon 2020, GBS-CIDP Foundation International, Baxalta, Grifols, CSL Behring, Annexon and Hansa Biopharma outside the submitted work; FE reports grants from ZonMw (Dutch Governmental Agency), non-financial support from Sanquin Blood Supply, during the conduct of this study; He also reports grants from CSL Behring, Kedrion, Terumo BCT and Takeda Pharmaceutical Company, outside the submitted work. Grants were paid to the institution and are used for investigator-initiated studies within INCbase, an international CIDP registry. In addition, he received a consultancy fee from UCB pharma, paid to the institution, outside the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Van den Bergh PY, Hadden RD, Bouche P, Cornblath DR, Hahn A, Illa I, Koski CL, Leger JM, Nobile-Orazio E, Pollard J, Sommer C, van Doorn PA, van Schaik IN, European Federation of Neurological S, Peripheral Nerve S European Federation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on management of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: report of a joint task force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society—first revision. Eur J Neurol. 2010;17(3):356–363. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2009.02930.x. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

