Nanotherapies for sepsis by regulating inflammatory signals and reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: New insight for treating COVID-19
- PMID: 34174559
- PMCID: PMC8205260
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102046
Nanotherapies for sepsis by regulating inflammatory signals and reactive oxygen and nitrogen species: New insight for treating COVID-19
Abstract
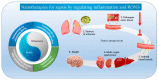
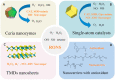
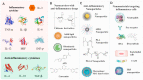
SARS-CoV-2 has caused up to 127 million cases of COVID-19. Approximately 5% of COVID-19 patients develop severe illness, and approximately 40% of those with severe illness eventually die, corresponding to more than 2.78 million people. The pathological characteristics of COVID-19 resemble typical sepsis, and severe COVID-19 has been identified as viral sepsis. Progress in sepsis research is important for improving the clinical care of these patients. Recent advances in understanding the pathogenesis of sepsis have led to the view that an uncontrolled inflammatory response and oxidative stress are core factors. However, in the traditional treatment of sepsis, it is difficult to achieve a balance between the inflammation, pathogens (viruses, bacteria, and fungi), and patient tolerance, resulting in high mortality of patients with sepsis. In recent years, nanomaterials mediating reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) and the inflammatory response have shown previously unattainable therapeutic effects on sepsis. Despite these advantages, RONS and inflammatory response-based nanomaterials have yet to be extensively adopted as sepsis therapy. To the best of our knowledge, no review has yet discussed the pathogenesis of sepsis and the application of nanomaterials. To help bridge this gap, we discuss the pathogenesis of sepsis related to inflammation and the overproduction RONS, which activate pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP)-pattern recognition receptor (PRR) and damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP)-PRR signaling pathways. We also summarize the application of nanomaterials in the treatment of sepsis. As highlighted here, this strategy could synergistically improve the therapeutic efficacy against both RONS and inflammation in sepsis and may prolong survival. Current challenges and future developments for sepsis treatment are also summarized.
Keywords: COVID-19; Inflammation; Nanotherapy; RONS; Sepsis.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest, financial or otherwise.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Pathogenesis-directed therapy of 2019 novel coronavirus disease.J Med Virol. 2021 Mar;93(3):1320-1342. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26610. Epub 2020 Nov 10. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 33073355 Review.
-
An Enzyme-Mimicking Single-Atom Catalyst as an Efficient Multiple Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species Scavenger for Sepsis Management.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Mar 23;59(13):5108-5115. doi: 10.1002/anie.201912182. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 31960567
-
Safety and Efficacy of Imatinib for Hospitalized Adults with COVID-19: A structured summary of a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2020 Oct 28;21(1):897. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-04819-9. Trials. 2020. PMID: 33115543 Free PMC article.
-
Sepsis Management, Controversies, and Advancement in Nanotechnology: A Systematic Review.Cureus. 2022 Feb 11;14(2):e22112. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22112. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35308665 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sustainable Nanosheet Antioxidants for Sepsis Therapy via Scavenging Intracellular Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species.ACS Nano. 2020 Aug 25;14(8):10324-10336. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c03807. Epub 2020 Aug 11. ACS Nano. 2020. PMID: 32806029
Cited by
-
Mitochondria-Targeting Chemodynamic Therapy Nanodrugs for Cancer Treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 10;13:847048. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.847048. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35222052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanodrugs Detonate Lysosome Bombs.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 17;13:909504. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.909504. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35656308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PRDM16 suppresses ferroptosis to protect against sepsis-associated acute kidney injury by targeting the NRF2/GPX4 axis.Redox Biol. 2024 Dec;78:103417. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103417. Epub 2024 Nov 7. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 39549609 Free PMC article.
-
Nanomaterial-based encapsulation of biochemicals for targeted sepsis therapy.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Jul 4;33:102054. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.102054. eCollection 2025 Aug. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40688672 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovering common pathogenetic processes between COVID-19 and sepsis by bioinformatics and system biology approach.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 31;13:975848. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.975848. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119022 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crunkhorn S. New route to sepsis therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019;18(4) 251-251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

