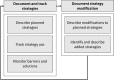
Strengthening methods for tracking adaptations and modifications to implementation strategies
- PMID: 34174834
- PMCID: PMC8235850
- DOI: 10.1186/s12874-021-01326-6
Strengthening methods for tracking adaptations and modifications to implementation strategies
Abstract
Background: Developing effective implementation strategies requires adequate tracking and reporting on their application. Guidelines exist for defining and reporting on implementation strategy characteristics, but not for describing how strategies are adapted and modified in practice. We built on existing implementation science methods to provide novel methods for tracking strategy modifications.
Methods: These methods were developed within a stepped-wedge trial of an implementation strategy package designed to help community clinics adopt social determinants of health-related activities: in brief, an 'Implementation Support Team' supports clinics through a multi-step process. These methods involve five components: 1) describe planned strategy; 2) track its use; 3) monitor barriers; 4) describe modifications; and 5) identify / describe new strategies. We used the Expert Recommendations for Implementing Change taxonomy to categorize strategies, Proctor et al.'s reporting framework to describe them, the Consolidated Framework for Implementation Research to code barriers / contextual factors necessitating modifications, and elements of the Framework for Reporting Adaptations and Modifications-Enhanced to describe strategy modifications.
Results: We present three examples of the use of these methods: 1) modifications made to a facilitation-focused strategy (clinics reported that certain meetings were too frequent, so their frequency was reduced in subsequent wedges); 2) a clinic-level strategy addition which involved connecting one study clinic seeking help with community health worker-related workflows to another that already had such a workflow in place; 3) a study-level strategy addition which involved providing assistance in overcoming previously encountered (rather than de novo) challenges.
Conclusions: These methods for tracking modifications made to implementation strategies build on existing methods, frameworks, and guidelines; however, as none of these were a perfect fit, we made additions to several frameworks as indicated, and used certain frameworks' components selectively. While these methods are time-intensive, and more work is needed to streamline them, they are among the first such methods presented to implementation science. As such, they may be used in research on assessing effective strategy modifications and for replication and scale-up of effective strategies. We present these methods to guide others seeking to document implementation strategies and modifications to their studies.
Trial registration: clinicaltrials.gov ID: NCT03607617 (first posted 31/07/2018).
Keywords: Implementation context; Implementation strategies; Modification and adaptation; Reporting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous