A newly identified linear epitope on non-RBD region of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein improves the serological detection rate of COVID-19 patients
- PMID: 34174835
- PMCID: PMC8234764
- DOI: 10.1186/s12866-021-02241-y
A newly identified linear epitope on non-RBD region of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein improves the serological detection rate of COVID-19 patients
Abstract
Background: Serological test is helpful in confirming and tracking infectious diseases in large population with the advantage of fast and convenience. Using the specific epitope peptides identified from the whole antigen as the detection antigen is sensitive and relatively economical. The development of epitope peptide-based detection kits for COVID-19 patients requires comprehensive information about epitope peptides. But the data on B cell epitope of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein is still limited. More importantly, there is a lack of serological data on the peptides in the population. In this study, we aimed to identify the B cell epitope peptides of spike protein and detect the reactivity in serum samples, for further providing data support for their subsequent serological applications.
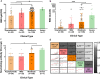
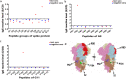
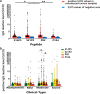
Results: Two B cell linear epitopes, P104 and P82, located in non-RBD region of SARS-CoV-2 S protein were identified by indirect ELISA screening of an overlapping peptide library of the S protein with COVID-19 patients' convalescent serum. And the peptides were verified by testing with 165 serum samples. P104 has not been reported previously; P82 is contained in peptide S21P2 reported before. The positive reaction rates of epitope peptides S14P5 and S21P2, the two non-RBD region epitopes identified by Poh et al., and P82 and P104 were 77.0%, 73.9%, 61.2% and 30.3%, respectively, for 165 convalescent sera, including 30 asymptomatic patients. Although P104 had the lowest positive rate for total patients (30.3%), it exhibited slight advantage for detection of asymptomatic infections (36.7%). Combination of epitopes significantly improved the positive reaction rate. Among all combination patterns, (S14P5 + S21P2 + P104) pattern exhibited the highest positive reaction rate for all patients (92.7%), as well as for asymptomatic infections (86.7%), confirming the feasibility of P104 as supplementary antigen for serological detection. In addition, we analyzed the correlation between epitopes with neutralizing antibody, but only S14P5 had a medium positive correlation with neutralizing antibody titre (rs = 0.510, P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Our research proved that epitopes on non-RBD region are of value in serological detection especially when combination more than one epitope, thus providing serological reaction information about the four epitopes, which has valuable references for their usage.
Keywords: Antibody; Epitopes; Humoral immunity; SARS-CoV-2; Spike protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Epitope-specific antibody responses differentiate COVID-19 outcomes and variants of concern.JCI Insight. 2021 Jul 8;6(13):e148855. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.148855. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 34081630 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of immunodominant epitopes on nucleocapsid and spike proteins of the SARS-CoV-2 in Iranian COVID-19 patients.Pathog Dis. 2022 Feb 9;80(1):ftac001. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftac001. Pathog Dis. 2022. PMID: 34994386 Free PMC article.
-
Epitope mapping of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein using naturally-acquired immune responses to develop monoclonal antibodies.Sci Rep. 2025 May 9;15(1):16269. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-00555-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40346118 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense Peptide Technology for Diagnostic Tests and Bioengineering Research.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 24;22(17):9106. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179106. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34502016 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scoping review of the applications of peptide microarrays on the fight against human infections.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 25;17(1):e0248666. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0248666. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35077448 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Promising Tool in Serological Diagnosis: Current Research Progress of Antigenic Epitopes in Infectious Diseases.Pathogens. 2022 Sep 25;11(10):1095. doi: 10.3390/pathogens11101095. Pathogens. 2022. PMID: 36297152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Peptides in Diagnostics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 17;22(16):8828. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168828. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of two linear epitopes SARS CoV-2 spike protein formulated in tandem repeat.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 20;18(1):e0280627. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280627. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36662754 Free PMC article.
-
Comirnaty-Elicited and Convalescent Sera Recognize Different Spike Epitopes.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Dec 1;9(12):1419. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9121419. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34960165 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of three conserved linear B cell epitopes on the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022 Dec;11(1):2120-2131. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2022.2109515. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2022. PMID: 35916768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Emeribe AU, Abdullahi IN, Shuwa HA, Uzairue L, Musa S, Anka AU, et al. Humoral immunological kinetics of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection and diagnostic performance of serological assays for coronavirus disease 2019: an analysis of global reports. Int Health. 2021. 10.1093/inthealth/ihab005. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rashid ZZ, Othman SN, Abdul Samat MN, Ali UK, Wong KK. Diagnostic performance of COVID-19 serology assays. Malays J Pathol. 2020;42:13–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

