Bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed genes and pathways in the development of cervical cancer
- PMID: 34174849
- PMCID: PMC8236200
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-08412-4
Bioinformatics analysis of differentially expressed genes and pathways in the development of cervical cancer
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to explore and identify key genes and signaling pathways that contribute to the progression of cervical cancer to improve prognosis.
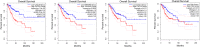
Methods: Three gene expression profiles (GSE63514, GSE64217 and GSE138080) were screened and downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database (GEO). Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened using the GEO2R and Venn diagram tools. Then, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses were performed. Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) was performed to analyze the three gene expression profiles. Moreover, a protein-protein interaction (PPI) network of the DEGs was constructed, and functional enrichment analysis was performed. On this basis, hub genes from critical PPI subnetworks were explored with Cytoscape software. The expression of these genes in tumors was verified, and survival analysis of potential prognostic genes from critical subnetworks was conducted. Functional annotation, multiple gene comparison and dimensionality reduction in candidate genes indicated the clinical significance of potential targets.
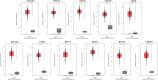
Results: A total of 476 DEGs were screened: 253 upregulated genes and 223 downregulated genes. DEGs were enriched in 22 biological processes, 16 cellular components and 9 molecular functions in precancerous lesions and cervical cancer. DEGs were mainly enriched in 10 KEGG pathways. Through intersection analysis and data mining, 3 key KEGG pathways and related core genes were revealed by GSEA. Moreover, a PPI network of 476 DEGs was constructed, hub genes from 12 critical subnetworks were explored, and a total of 14 potential molecular targets were obtained.
Conclusions: These findings promote the understanding of the molecular mechanism of and clinically related molecular targets for cervical cancer.
Keywords: Bioinformatics analysis; Cervical cancer; Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia; Differentially expressed genes; Functional enrichments.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he/she has no competing interests.
Figures












Similar articles
-
Bioinformatics analyses of significant genes, related pathways and candidate prognostic biomarkers in glioblastoma.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Nov;18(5):4185-4196. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9411. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 30132538 Free PMC article.
-
The identification of key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma by bioinformatics analysis of high-throughput data.Med Oncol. 2017 Jun;34(6):101. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-0963-9. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Med Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28432618 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated bioinformatics analysis for the screening of hub genes and therapeutic drugs in ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2020 Jan 27;13(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13048-020-0613-2. J Ovarian Res. 2020. PMID: 31987036 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analyses of potential key genes in active tuberculosis: A systematic review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 Jul 30;100(30):e26582. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000026582. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 34397688 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of common core ion channel genes in epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease.Ir J Med Sci. 2024 Feb;193(1):417-424. doi: 10.1007/s11845-023-03447-x. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Ir J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 37477849 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering Immunotoxicity in Animal-Derived Biomaterials: A Genomic and Bioinformatics Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10963. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010963. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456747 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel potential drugs for the treatment and prevention of osteoarthritis.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024 Jan 21;37:101647. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2024.101647. eCollection 2024 Mar. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 38304574 Free PMC article.
-
Tendomodulin in pan-cancer analysis: exploring its impact on immune modulation and uncovering functional insights in colorectal cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 11;25(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13608-z. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39934677 Free PMC article.
-
Whole Transcriptome Analysis of Intervention Effect of Sophora subprostrate Polysaccharide on Inflammation in PCV2 Infected Murine Splenic Lymphocytes.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023 Jul 20;45(7):6067-6084. doi: 10.3390/cimb45070383. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37504299 Free PMC article.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Protein Complex Regulates Cancer Stem Cells and is Associated with Sorafenib Resistance in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Aug 9;11:1519-1539. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S474343. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 39139735 Free PMC article.
References
-
- den Boon JA, Pyeon D, Wang SS, Horswill M, Schiffman M, Sherman M, Zuna RE, Wang Z, Hewitt SM, Pearson R, Schott M, Chung L, He Q, Lambert P, Walker J, Newton MA, Wentzensen N, Ahlquist P. Molecular transitions from papillomavirus infection to cervical precancer and cancer: role of stromal estrogen receptor signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(25):E3255–E3264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1509322112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

