Predictive model based on gene and laboratory data for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in Kawasaki disease in a Chinese population
- PMID: 34174887
- PMCID: PMC8236184
- DOI: 10.1186/s12969-021-00582-6
Predictive model based on gene and laboratory data for intravenous immunoglobulin resistance in Kawasaki disease in a Chinese population
Abstract
Background: Here, we investigated the predictive efficiency of a newly developed model based on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and laboratory data for intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) resistance in Kawasaki disease (KD) in a Chinese population.
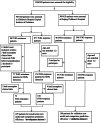
Methods: Data relating to children with KD were acquired from a single center between December 2015 and August 2019 and used to screen target SNPs. We then developed a predictive model of IVIG resistance using previous laboratory parameters. We then validated our model using data acquired from children with KD attending a second center between January and December 2019.
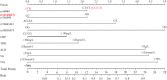
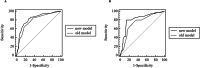
Results: Analysis showed that rs10056474 GG, rs746994GG, rs76863441GT, rs16944 (CT/TT), and rs1143627 (CT/CC), increased the risk of IVIG-resistance in KD patients (odds ratio, OR > 1). The new predictive model, which combined SNP data with a previous model derived from laboratory data, significantly increased the area under the receiver-operator-characteristic curves (AUC) (0.832, 95% CI: 0.776-0.878 vs 0.793, 95%CI:0.734-0.844, P < 0.05) in the development dataset, and (0.820, 95% CI: 0.730-0.889 vs 0.749, 95% CI: 0.652-0.830, P < 0.05) in the validation dataset. The sensitivity and specificity of the new assay were 65.33% (95% CI: 53.5-76.0%) and 86.67% (95% CI: 80.2-91.7%) in the development dataset and 77.14% (95% CI: 59.9-89.6%) and 86.15% (95% CI: 75.3-93.5%) in the validation dataset.
Conclusion: Analysis showed that rs10056474 and rs746994 in the SMAD5 gene, rs76863441 in the PLA2G7 gene, and rs16944 or rs1143627 in the interleukin (IL)-1B gene, were associated with IVIG resistant KD in a Chinese population. The new model combined SNPs with laboratory data and improved the predictve efficiency of IVIG-resistant KD.
Keywords: Intravenous immunoglobulin resistance; Kawasaki disease; Single nucleotide polymorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Bar-Meir M, et al. Prediction of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin in children with Kawasaki disease. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2018;7(1):25–29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

