Rapid and precise diagnosis of pneumonia coinfected by Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus fumigatus assisted by next-generation sequencing in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report
- PMID: 34174895
- PMCID: PMC8235577
- DOI: 10.1186/s12941-021-00448-5
Rapid and precise diagnosis of pneumonia coinfected by Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus fumigatus assisted by next-generation sequencing in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus: a case report
Abstract
Background: Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus fumigatus, are opportunistic pathogenic fungus that has a major impact on mortality in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. With the potential to invade multiple organs, early and accurate diagnosis is essential to the survival of SLE patients, establishing an early diagnosis of the infection, especially coinfection by Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus fumigatus, still remains a great challenge.
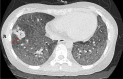
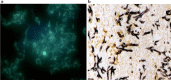
Case presentation: In this case, we reported that the application of next -generation sequencing in diagnosing Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus fumigatus coinfection in a Chinese girl with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Voriconazole was used to treat pulmonary aspergillosis, besides sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim (SMZ-TMP), and caspofungin acetate to treat Pneumocystis jirovecii infection for 6 days. On Day 10 of admission, her chest radiograph displayed obvious absorption of bilateral lung inflammation though the circumstance of repeated fever had not improved. Unfortunately, the patient discharged from the hospital since the financial burden, and during the follow-up, it was documented the patient died within one week after discharge.
Conclusions: This successful application of the next generation sequencing assisting the rapid diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus fumigatus coinfection provides a new perspective in the clinical approach against the systematic fungi infections and highlights the potential of this technique in rapid etiological diagnosis.
Keywords: Aspergillus fumigatus; Case report; Next generation sequencing; Pneumocystis jirovecii.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pulmonary co-infections by Pneumocystis jirovecii and Aspergillus fumigatus in non-HIV patients: A report of two cases and literature review.Mycoses. 2017 Oct;60(10):626-633. doi: 10.1111/myc.12642. Epub 2017 Jun 28. Mycoses. 2017. PMID: 28660636 Review.
-
A co-infection of varicella-zoster virus and Pneumocystis jirovecii in a non-HIV immunocompromised patient: a case report.BMC Infect Dis. 2019 Dec 30;19(1):1092. doi: 10.1186/s12879-019-4715-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2019. PMID: 31888503 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in systemic lupus erythematosus from southern Taiwan.J Clin Rheumatol. 2013 Aug;19(5):252-8. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0b013e31829d5017. J Clin Rheumatol. 2013. PMID: 23872548
-
[Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in a Patient with Interstitial Lung Disease].Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 2015 Mar;39(1):66-9. doi: 10.5152/tpd.2015.3476. Turkiye Parazitol Derg. 2015. PMID: 25917588 Turkish.
-
Pneumocystis jirovecii and Nocardia pneumonia in a middle-aged male with Nephrotic syndrome: a case report and literature review.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Sep 30;24(1):1071. doi: 10.1186/s12879-024-09987-6. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39350124 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in critically pediatric patients.Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2023 Jan 16;22(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12941-023-00555-5. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. 2023. PMID: 36647095 Free PMC article.
-
Pneumonia Caused by Coinfection with Cytomegalovirus and Pneumocystis jirovecii in an HIV-Negative Infant Diagnosed by Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Jun 30;15:3417-3425. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S364241. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 35800120 Free PMC article.
-
Aspergillus fumigatus escape mechanisms from its harsh survival environments.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Dec;108(1):53. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12952-z. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38175242 Review.
-
Fungal gut microbiota dysbiosis in systemic lupus erythematosus.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 5;14:1149311. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1149311. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37089568 Free PMC article.
-
Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for the diagnosis of pulmonary aspergillosis in non-neutropenic patients: a retrospective study.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Aug 1;12:925982. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.925982. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35979088 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

